How KYB Would Have Stopped The Laundromat Movie From Happening
November 28, 2020
13 minutes read
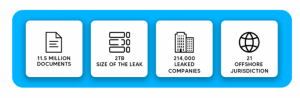
The Panama Papers incident highlights one of the most significant financial leaks in the last decade. It refers to the 11.5 million leaked encrypted confidential documents of Panama-based law firm Mossack Fonseca. These files were made public on April 3, 2016 by the German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung (SZ). They had christened the name as the “Panama Papers.”
The documents revealed the active network of more than 214,000 tax havens. These involved people and entities across 200 different nations. A joint effort was made by SZ and the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) for a year to decipher the encrypted files. The files furnish detailed information about thousands of offshore “shell” companies. These were used by some of the world’s most influential people to conceal wealth or avoid paying taxes.
Mossack Fonseca was established in 1977 by Jurgen Mossack and Ramon Fonseca. The firm was one of the top offshore legal services providers until April 2016.
The Panama Papers allegedly reveal a global system of undisclosed offshore accounts, money laundering and tax evasion. They displayed how influential people around the world use shell companies to conceal assets. They can also be involved in possible illegal activity.
The Source of the Name “Panama Papers”
The files have been given the moniker “Panama Papers” due to the country of origin. However, the government of Panama has vehemently objected to the name. This is because it seems to put some blame or negative association on the country itself. This is despite any involvement of the government in the actions of Mossack Fonseca. Nonetheless, the nickname has become widespread. However, some media outlets that have covered the story have designated them as the “Mossack Fonseca Papers.”
The incident is the greatest disclosed data breach around a law firm. After the incident, founding partner Ramon Fonseca and other public sources stated that the firm’s network had been jeopardized by hackers sometime in 2015. Security researchers identified numerous unpatched vulnerabilities in Mossack’s website and email server. These could have been very easily compromised by hackers. A total of 2.6 terabytes of data — including 4.8 million emails, 3 million database files, and 2.1 million.pdf files — were leaked. including client documents dating back to the 1970s.
Main Highlights
- The Panama Papers were a massive leak of financial files from the database of Mossack Fonseca. This firm was the fourth-biggest offshore law firm in the world.
- The documents were leaked anonymously to German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung (SZ), which released them on April 3, 2016.
- The files date back to as far as the 1970s. They shed light on a network of 214,000 tax-havens. These involve wealthy people, public officials, and entities across 200 nations.
- The confidential documents were made public by the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ). The body is a non-profit organization based in Washington. It said that the documents contain details of both current and former world leaders. Other important people include businessmen, criminals, celebrities and sportsmen.
- A majority of the files showed no illegal activity. However, some of the shell corporations were for fraud, tax evasion, or avoiding international sanctions.
- The ICIJ’s website lists banks including HSBC, UBS, Credit Suisse, Deutsche Bank who have utilized Mossack Fonseca. They used the firm to create offshore accounts.
The Truth In Netflix — How The Story Goes Hollywood
The Panama Papers scandal had a multifold impact on nations. It enhanced the national and global focus on the overall harm of money laundering, tax evasion, and terrorist financing. The incident also helped propel the international critique of USA as a potential haven for money laundering and tax evasion. This is mainly due to provisions in the U.S. to form legal entities. Such entities are formed without having to disclose the identity of true beneficial owners. It also showed the world how lawyers can facilitate their clients’ money laundering.
The somber reality sure caught the attention of Steven Soderbergh. he soon went on to direct the recently launched Netflix-original “The Laundromat”. The movie revolves around the main protagonists of the Panama Papers incident
– Jurgen Mossack (portrayed by Gary Oldman)
and Ramon Fonseca (illustrated by Antonio Banderas).

“How do 15 million millionaires in 200 countries stay rich? With lawyers like these — “ The trailer of the movie “The Laundromat” itself hints to a satirical flavor and adds to the point we mentioned earlier. Many people may find knowledge through humor in the movie. But the original characters certainly don’t share that perspective. The movie has been subject to an extensive lawsuit by the original duo. They have cited the grounds of the movie as “defamatory”
The incident and resulting scandal also illustrates another looming threat. The growing frequency, ease, and potentially devastating consequences of data breaches are concerning. Cyber attacks can threaten even the richest and most powerful people. The breach of client confidential information held by a law firm can have serious potential legal consequences. This applies to both the firm and its affected clients.
The Impact On The Indian Subcontinent

The Indian Express was the partner of the ICIJ project on the Panama Paper Leaks. They had revealed the names of over 500 Indians in its report. This came after 8 months of an extensive investigation of over 36,000 files.
The list publishes the names of corporate figures like the DLF owner K P Singh and nine of his family members. Other names include the Indiabulls Sameer Gehlaut, Vinod Adani who is also a businessman and the elder brother of Gautam Adani. India-born Dutch businessman Ratan Chadha who is the founder of Mexx clothing is also mentioned in the list.
- The list provides details of big businessmen to celebrities of Bollywood and politicians. Top names from Bollywood include Amitabh Bachchan & Aishwarya Rai Bachchan.
- Mohan Lal Lohia, Abdul Rashid and others are also named among others in this context. The list also shows the addresses of businessmen in Panchkula, Dehradun, Vadodara and Mandsaur. It also includes cricket franchise deals. The files indicate linkages of those people who are already under the scrutiny of the CBI and Income Tax department.
- The main accusation against Indians is that they propped up their offshore companies long before the rules were changed in 2013. it was with the intention to place foreign exchange in a tax haven.
Violations of Indian Laws Under Panama Papers Leak
There are mainly laws which are being violated in the Panama Papers case which have been found under the investigation,
- The Incorporation of Companies Overseas.
- Acquisition of the majority shares of overseas companies in contravention of FEMA rules.
- Violation of RBI’s Liberalised Remittance Scheme.
According to Indian legislation, Indians could not incorporate companies outside India. This is because remittances to foreign countries were not allowed before 2004. RBI in 2004 introduced a scheme called as Liberalised Remittance Scheme. This permitted individuals to remit upto $250,000 in phases. These remittances could be utilized for different reasons. Examples — medical, gifting, buying shares, etc.
The people were facing a lot of confusion on this issue. So, the RBI issued a notification in the year 2010. This stated that though the Liberalised Remittance Scheme, Indians are allowed to buy shares. However, it specifically prohibits the setting up of companies abroad by individuals.
RBI issued another notice in 2013. It allowed resident Indians to invest in joint ventures through the Overseas Direct Investment route. So, any company overseas by an Indian can be considered legal only if it was established after 2013.
Insurance Swindles, Shares Fraud and Money Laundering — The Stark Realities Of The Panama Papers
Take One (Insurance Fraud):
The Laundromat portrays the impact on individual lives with respect to the business handled by Mossack Fonseca. The first incident revolves around Ellen Martin (portrayed by Meryl Streep) and her husband (played by James Cromwell). Ellen Martin and her husband Joe are on a pleasure boat at Lake George, New York when it capsizes, drowning Joe. Ellen tries to get compensation from the boating company for Joe’s death. But she could not do so. The reinsurance company that the boat company’s owner and son Matthew bought their policy from was sold to another company based out of Nevis. The Nevis-based company is actually a trust of one of Mossack’s shell companies. It was under investigation by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for fraud. Several attempts to contact Mossack and the Nevis-based company were unsuccessful. Ellen travels to Nevis to confront Malchus Boncamper, the manager of the trust. Malchus tricks Ellen and escapes to Miami. But on the way he is caught and arrested by IRS-CI Special Agents at a Miami airport.
Take Two (Shell Shock — Bogus Shares)
The second story is about Simone, who is the daughter of Charles, an African billionaire. Simone discovers her best friend is having an affair with Charles. He offers her shares (supposedly worth $20 million) in one of his investment companies to keep her silent. She accepts his offer. But when she with her mother travels to Mossack’s offices in Panama City to claim the shares, they turn out to be worthless. This is because they are actually part of a shell company under Mossack that only exists on paper. The companies individual values turn out to be $100 and $27 each!!
Take Three (Money Laundering)
The third story is a dramatization of the death of Neil Heywood, part of the Wang Lijun incident. Heywood (renamed “Maywood” in the film), is an intermediary for wealthy Chinese looking to funnel money abroad. He visits a Chongqing hotel to meet Gu Kailai. Maywood demands and pressures Gu for a much higher price. This is if she wants him to continue laundering money for her family through a shell company Mossack owns. Gu responds by poisoning Maywood’s drinks. Gu discloses the incident and reports Maywood to Chongqing police chief Wang Lijun. He secretly records the conversation; he then reports her to the Chinese government.
The story ends with the arrest of Gu and her husband Bo Xilai for Maywood’s murder and for corruption in connection to The Wang Lijun incident. It was a major Chinese political scandal which began in February 2012. This was when Wang Lijun, vice-mayor of Chongqing, was abruptly demoted. He had revealed the details of British businessman Neil Heywood’s murder and subsequent cover-up to the US Consulate.
Interestingly, Neil Haywood, was depicted as a shark in the shell company game through the movie but not much details were provided about him. A point to be noted here is that the film is vague about the reasons why the offshore world thrives. It bludgeons its message home as a “haves vs have-nots” narrative. The particular focus is on tax evasion. This misses some of the other reasons that AML practitioners should be concerned about offshore companies.
KYB — Why It Would Have Been The Anti-Laundromat?
Besides legal considerations, there are also social and ethical responsibilities for knowing UBO. It means the ultimate beneficial owners (UBO) of companies you are doing business with. The Panama Papers disclosed over 200,000 shell companies that hid billions of dollars from lawful taxation. These hidden funds go into the hands of already influential people . In turn, it creates a larger tax burden for society.
Implementing Know Your Business (KYB) requires investigating the UBO structure by law. This is part of the customer due diligence (CDD) process.
KYB in Europe
For example the 4th AML Directive is already in effect in Europe and requires:
identifying the beneficial owner and taking reasonable measures to verify that person’s identity. In this way, the obliged entity is satisfied that it knows who the beneficial owner is. UBO includes legal persons, trusts, companies, foundations and similar legal arrangements. KYB takes reasonable measures to understand the ownership and control structure of the customer.
A beneficial owner in the EU is an entity/individual who owns more than 25% of the corporate entity. Currently the EU customer due diligence requirements are:
(a) identifying the customer and verifying the customer’s identity. This can be done on the basis of documents, data or information procured from a reliable and independent source.
(b) identifying the beneficial owner to the extent that the obliged entity is satisfied. It knows who the beneficial owner is.
© assessing and obtaining information. This is done as required on the purpose and intended nature of the business relationship.
(d) monitoring of the business relationship including scrutiny of transactions. This includes all transactions undertaken throughout the course of that relationship. It ensures that the transactions being conducted are consistent with the obliged entity’s knowledge of the customer, the business and risk profile.
KYB in the US
In the US, the Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Final Rule went into full effect May 11, 2018. It states that all covered financial institutions must identify and verify the identity of the beneficial owners of all legal entity customers (other than those that are excluded) at the time a new account is opened (other than accounts that are exempted). Financial institutions (FIs) includes banks; brokers or dealers in securities, mutual funds; and futures commission merchants and introducing brokers in commodities.
Unfortunately, different jurisdictions have different requirements. Even within the same jurisdictions different regulations are applicable. For example, besides the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), which covers the CDD rules, US FIs also have to consider Dodd-Frank, SEC disclosure rules, OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control), and FACTA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act).
Conclusion
The Laundromat may appear entertaining to many a Netflix enthusiast, but the mortifying part is that it is based on true events. Previously we have encountered movies like The Big Short, The Wolf Of Wall Street and many such titles. These have been entertaining and devastating at the same time. You often love to see and hear about the ways that con man take money, but we often forget that in many cases, its YOUR money that is getting taken and it is YOU that gets scammed.
But there is hope — once KYB comes into full sway. The enforcement and regulatory authorities will finally have the trail to follow fake organizations and prevent hundreds of millions of dollars worth of economic offenses in the form of financial fraud. Yes, you might not have an original classic like The Laundromat, but at least your money will be safe — and then you can always turn to Ocean’s Trilogy for a similar experience, only fictional.
About Signzy
Signzy is a market-leading platform redefining the speed, accuracy, and experience of how financial institutions are onboarding customers and businesses – using the digital medium. The company’s award-winning no-code GO platform delivers seamless, end-to-end, and multi-channel onboarding journeys while offering customizable workflows. In addition, it gives these players access to an aggregated marketplace of 240+ bespoke APIs that can be easily added to any workflow with simple widgets.
Signzy is enabling ten million+ end customer and business onboarding every month at a success rate of 99% while reducing the speed to market from 6 months to 3-4 weeks. It works with over 240+ FIs globally, including the 4 largest banks in India, a Top 3 acquiring Bank in the US, and has a robust global partnership with Mastercard and Microsoft. The company’s product team is based out of Bengaluru and has a strong presence in Mumbai, New York, and Dubai.
Visit www.signzy.com for more information about us.
You can reach out to our team at reachout@signzy.com
Reach us at: www.signzy.com
Written By:
Signzy
Written by an insightful Signzian intent on learning and sharing knowledge.














