In this technology-driven world, Deepfake is everywhere.
Deepfake has gone from being meme material to becoming a serious concern for businesses.
Any sector that interacts remotely with customers is vulnerable to deepfakes.
But why and how?
Deepfake: a serious concern
Deepfakes are superior versions of photoshopped images/audios/videos using AI-driven methodology.
Put otherwise, a deepfake appears to be a real person’s recorded face and voice, but the words they seem to be speaking were not spoken by them in reality.
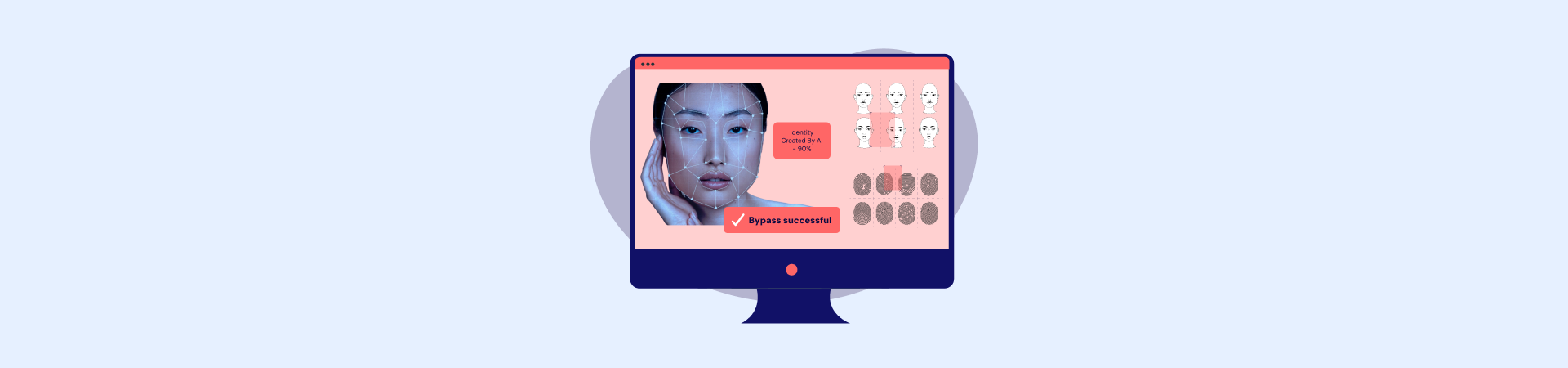
Since the introduction of facial biometric verification, fraudsters have been in constant search for ways to bypass it—from simple handmade masks to advanced deepfake technology.
As AI flourishes, cybercriminals can now easily create complex tools such as deepfakes, which are synthetic pictures that remarkably resemble actual human faces, circumventing security mechanisms.
How? By taking advantage of the static nature of physical attributes like fingerprints, facial shapes, and eye sizes that are employed for identification.
Basic biometric systems allow access to authorized users using hardware and software.
How do they generally determine who has access to the things that the security system protects? Through scanning faces, fingerprints, irises, and voice tones.
Deepfake technology might not be able to outperform developing security systems if it replicates such data slowly. But deepfake technology advances quickly.
It is believed that deepfakes are present in about 25% of fake news generated online.
How Deepfakes trick biometrics
Social media has made it possible for scammers to get almost anyone’s photo and use it to circumvent identity verification.
Therefore, fraudsters may easily utilize social media photographs to steal devices and accounts if face biometric technology is unable to assess specific aspects of an image.
There are a few ways deepfakes can trick biometric security technologies.
Therefore, understanding how they do it is the first step toward finding solutions.
One way to bypass biometrics is Camera injection.
It occurs when a criminal disables a camera’s charged-coupled device, popularly known as CCD, to insert pre-recorded footage, a live face-swap video stream, or entirely bogus material created with deepfake technology.
The primary risk is that, by using camera injection, fraudsters can remain unnoticed without victims knowing about the hack. The ones with malicious intent can cause The ones with malicious intent can cause substantial damage by stealing identity, making fake accounts, or doing fraudulent transactions.
💡 Related Blog: How Fraudsters Leverage AI and Deepfakes for Identity Fraud
Another way to bypass biometrics is by taking advantage of static data.
Static Data? Any data derived from a person’s traits that remain constant, such as one’s facial shape or eye size. If someone is using a fingerprint scanner, it may also examine fingerprints. Since they never need to be updated, any of these static features are simple to duplicate.
Due to AI, it has also become quite easy to replicate vocal tones.
The AI behind deepfakes can copy sounds and reproduce them exactly. The program will break down the person’s accent and voice tone into smaller clips and put them into the system’s neural network if you upload a video of yourself speaking.
Likewise, AI systems can keep voices over time. It can replicate the voice data files, should a cybercriminal want to employ one to pose as a deepfake. The deepfake utilizes its algorithms to speak the response when a security system asks a person who appears to be genuine for a stored password or keyword.
One would assume that it would be hard to fool a verification device that requires users to make erratic motions like blinking or winking. Sadly, this is untrue since motions can be pre-recorded, and certain verification algorithms are unable to identify these kinds of movies
With Deepfake technology, face recognition can be readily circumvented.
Yes. Face-swapping someone to access their account is simple since anybody can use free generators to construct a deepfake for little to no money.
However, by examining artefacts in the supplied image, a proficient deepfake detection system would be able to identify deepfakes.
But how do biometric security measures hold up against deepfakes?
Mentioned below are a few ways that are easy and difficult for the potential AI threat to beat.
-
Algorithms for facial biometry: Simple to Override
A face detection scanner is likely to be cracked if someone hacks it and places a deepfake in front of it. It confirms the identification of the deepfake using the static data kept in its system.
In the absence of layered liveness verification, deepfakes might be mistaken for the real user of the system by systems like iris recognition.
Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) is essential due to this additional weak point. The system is compatible with any device that has internet access, and MFA will allow biometric authentication methods to catch up.
With a single click, data theft can be stopped using a warning signal whenever someone attempts to access your restricted accounts from a different location or device.
-
Voice-controlled Security Systems: Difficult to Override
If you follow industry experts and read about the newest developments in security systems, you may be shocked to learn that voice-controlled biometric devices are harder for deepfakes to fool.
Voice activation is frequently used in conjunction with freshly created authentication questions that the AI is unable to figure out previously. More sophisticated security systems could also be able to detect vocal cord-only swaying in sound.
-
Fingerprint Scanners: Not possible to Override
Since deepfakes are all digital, they are considerably harder to fool fingerprint sensors.
To avoid being detected by the scanner’s software, the AI would have to compromise it and pretend to be acceptable data. Scanners use heat to confirm that a finger is placed on its surface. Deepfakes can mimic fingerprints, but they are not able to produce heat that is comparable to that of a human hand.
Bypassing liveness does not include impersonation. Rather, criminals alter or replace biometric data to compromise the liveness system itself.
Every liveness technology has three vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might exploit:
- The gadget that the user uses to complete the biometric verification
- Active internet connection that allows the user’s biometric info to be sent to the server
- The server that verifies biometric info
A phone camera may be hijacked by fraudsters, who can then insert a deepfake or video already recorded. If data is not adequately secured when delivered over the internet, it can potentially be intercepted, and a server can be hacked.
How to protect yourself from AI-generated deepfakes?
To strengthen countermeasures against the risks associated with AI-generated deepfakes, organizations are encouraged to work with suppliers who exhibit a commitment to going above and beyond current security requirements.
Strengthening defenses against deepfakes and other types of fraud may be achieved by implementing solutions such as our all-in-one security platform with identity protection or our personal data cleansing solutions. The world of digital is changing. Fortunately, you can as well.