Understanding Customer Reverification: A Comprehensive Guide
November 25, 2024
6 minutes read
- Customer reverification is a continuous and ongoing process that helps businesses stay compliant and secure.
- The reverification process must be streamlined as inefficiencies can lead to poor user experience and customer drop-offs.
- Customer reverification has various types like government ID verification, 2-factor authentication, selfie verification, and more.
In today’s interconnected digital world, verifying a customer’s identity is no longer a one-time task. Businesses must ensure that customer information remains accurate and secure throughout their relationship. This process, known as reverification, goes beyond initial onboarding and plays an important role in regulatory compliance and fraud prevention.
Whether you’re a financial institution adhering to stringent Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations or an e-commerce platform handling sensitive customer data, reverification ensures a robust layer of security. But what is reverification, and why is it critical for businesses today? Let us understand reverification meaning, importance, and implementation.
What is Reverification?
Reverification refers to the process of re-confirming the identity and details of a customer who has already undergone an initial verification process. Unlike verification, which is typically a one-time process during onboarding, reverification is ongoing and ensures the accuracy of information over time.
For example, consider a bank customer who initially submitted their address proof during account creation. If the document used as address proof expires, or the customer moves to a new location, the bank will need to reverify their address to maintain updated records.
When Does Reverification Take Place?
Reverification is not a random process; it is triggered by specific events or circumstances, such as:
- Document Expiry: When identity documents like passports or driving licenses expire.
- Suspicious Activity: Unusual transactions or logins from unfamiliar locations may indicate fraudulent activity.
- Changes in Key Information: Updates to personal details, such as phone numbers or email addresses.
- Dormant Accounts: If a customer reactivates an account after a long period of inactivity.
- High-Risk Transactions: When customers engage in large or unusual financial transactions.
- Regulatory Changes: When laws or compliance requirements are updated.
By performing reverification at these critical moments, your business can proactively prevent fraud, ensure compliance, and maintain customer trust.
Why is Reverification Important?
Reverification is not just a formality; it plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of business processes. Here’s why it’s essential:
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries, such as banking, insurance, and healthcare, are bound by Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. These laws require businesses to monitor and verify customer identities continuously. Reverification ensures that businesses meet these regulatory requirements and avoid legal penalties.
Fraud Prevention
In the age of cybercrime, fraudsters often exploit outdated customer information to gain unauthorized access. Reverification acts as a safeguard, identifying suspicious activities and preventing fraud before it occurs.
Maintaining Accurate Records
Customer details such as addresses, employment status, and financial information can change over time. Reverification ensures that businesses always have the latest data, which is essential for offering personalized services and managing risks effectively.
Building Customer Trust
When businesses prioritize security and compliance, it demonstrates their commitment to protecting customer interests. A robust reverification process reassures customers that their data and transactions are in safe hands.
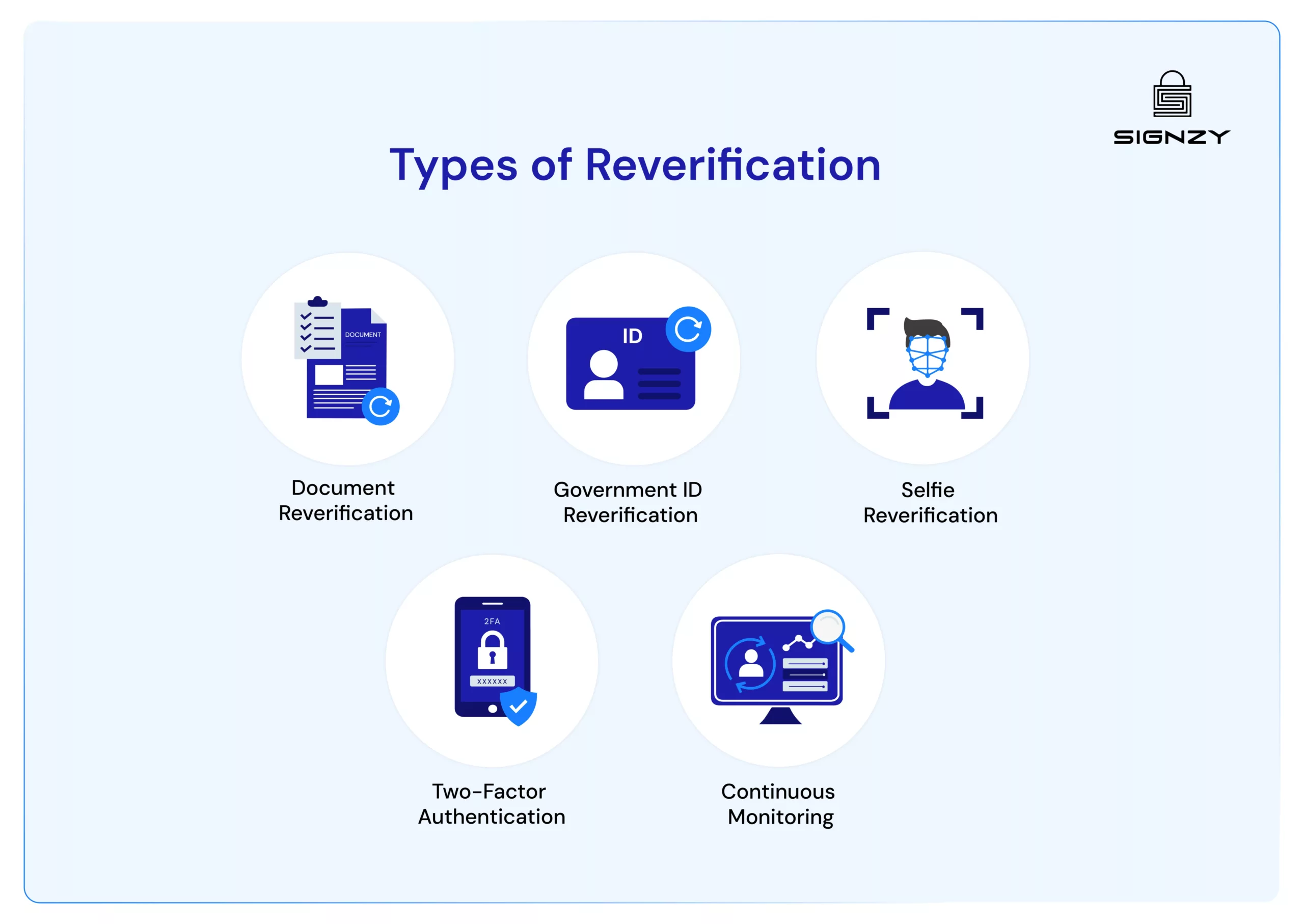
Types of Reverification
Depending on the business needs and industry, reverification can take different forms. Here are the key types:
- Document Reverification: This involves validating customer-provided documents, such as proof of address, income, or employment. For example, a bank may require customers to reverify their address proof every 12 months to maintain compliance.
- Government ID Reverification: Government-issued IDs like passports or driving licenses are critical for identity verification. Businesses reverify these documents when they expire or if a customer updates their ID details.
- Selfie Reverification: Biometric technology is often used to ensure real-time identity verification. Customers may be asked to upload a selfie, which is compared to their previous records to confirm their identity. This method is particularly useful in preventing fraud in high-risk industries.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security, 2FA involves verifying identity through two methods, such as a password and a one-time password (OTP) sent to the user’s mobile device.
- Continuous Monitoring: Businesses continuously monitor customer activities, rescreening them against updated sanctions lists, adverse media reports, and politically exposed persons (PEPs) databases. This ensures compliance and accurate risk assessment.
Benefits of Reverification for Businesses
Implementing reverification offers several advantages, including:
- Enhanced Security: Reverification protects businesses from unauthorized access and fraudulent activities, ensuring secure transactions.
- Regulatory Compliance: By keeping customer information up-to-date, businesses can easily meet evolving legal requirements and avoid penalties.
- Risk Management: Reverification helps businesses assess customer activities, flagging any irregularities that may indicate financial crimes.
- Improved Customer Experience: A transparent and seamless reverification process builds customer trust and loyalty, encouraging long-term engagement.
Challenges of Reverification
While beneficial, reverification also comes with challenges:
- Friction in Customer Experience: Reverification can disrupt the user journey if not executed smoothly. Customers may find repeated identity checks inconvenient.
- Operational Complexity: Managing large-scale reverification processes requires advanced tools and technology, which may involve high costs.
- Dynamic Regulations: Keeping up with constantly changing compliance requirements can be a challenge, especially for global businesses.
Implementing a Seamless Reverification Process
To address the challenges of reverification, businesses can adopt the following strategies:
- Automating the Process: Businesses can automate reverification tasks using AI-driven tools, ensuring faster and more accurate identity checks.
- Tailoring the Process: Customizing reverification workflows based on customer profiles and risk levels minimizes unnecessary friction.
- Combining Methods: Integrating multiple verification methods, such as biometric and document checks, enhances security without compromising the user experience.
Thankfully, Signzy has a varied selection of APIs that can help with the Identity Verification and Reverification process. From Face Match and Liveness Check to Criminal Screening and PEP Screening, Signzy’s API Marketplace ensures that your business has a robust identity verification ecosystem.
Conclusion
Reverification is more than a compliance requirement; it is a strategic approach to securing customer relationships and ensuring business integrity. By staying proactive and adopting efficient reverification practices, businesses can protect themselves from fraud, maintain regulatory compliance, and foster customer trust.
As digital transactions grow, so does the importance of keeping customer data accurate and secure. By implementing a well-thought-out reverification process, businesses can ensure a safe and seamless experience for their customers while staying ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is reverification in business?
Reverification is an ongoing and continuous process of checking and updating a business’ customers’ identity credentials.
What is the process of reverification?
The process of reverification includes updating and authenticating the customers’ credentials on a recurring basis.
What is the difference between verification and reverification?
Verification is a process that takes place during the onboarding of customers. Reverification is an ongoing process that continues for as long as the customer is associated with the business.