Passwordless Authentication: Methods, Benefits, and Use Cases
January 23, 2025
7 minutes read
- Passwordless authentication offers a solution to the growing problem of “secrets fatigue” by eliminating the need for users to remember and manage numerous complex passwords.
- While offering significant advantages in terms of user experience and security, passwordless authentication also presents challenges, such as the need for compatible devices and potential vulnerabilities in biometric data storage.
- The trend towards passwordless authentication is gaining momentum, with Microsoft reporting 2 million passwordless sign-ins per month via Windows Hello in early 2023.
Remember opening your first bank account? Walking into the branch, showing your ID, maybe signing a few papers. The bank knew it was you because they could see you, check your documents, match your signature. Simple, secure, human.
But when it comes to digital security, we’ve somehow made things more complicated.
We’ve replaced that natural verification process with strings of characters we call passwords – asking humans to remember what machines can easily crack.
What if securing digital access could feel as natural as that in-person bank visit?
Thankfully, passwordless authentication is possible at present.
Using what makes you uniquely you – your fingerprint, face, or personal device – brings that same level of natural security to the digital world.
If you are wondering how it works, you’re at the right spot! This guide explains everything about passwordless authentication – from how it works to choosing the right method for your needs.
But first, here are nuts-and-bolts.
What is Passwordless Authentication?
As the name implies, passwordless authentication eliminates the need for traditional passwords by verifying user identity through biometrics, security keys, or device verification. Instead of typing passwords, users can simply scan their fingerprints, look at their cameras, or approve a push notification to gain access.
As per SpyCloud, 64% of users still reuse their passwords across multiple accounts. Due to this, even a single account compromise will create a domino effect and make everything vulnerable.
Guess what? Cybercriminals can’t steal what isn’t there – no stored passwords means no password database to breach.
Core Benefit of Passwordless Authentication
Instead of relying on “something you know” (like a password), passwordless methods use “something you have” (your device) combined with “something you are” (your biometrics) or “something you possess” (a security key). This creates a much stronger security barrier that’s also easier to use.
How Exactly Does Passwordless Authentication Work?
So, how does passwordless authentication actually work? Here’s the straightforward process:
- When you try to log in, the authentication system creates a unique challenge
- Your device receives this challenge and asks you to prove your identity
- You verify yourself using your fingerprint, face scan, or security key
- Your device uses this verification to sign the challenge with a private cryptographic key
- The server confirms your identity by matching this signature with your public key
The real change happens through public key cryptography, which creates a secure connection without sharing any secrets.
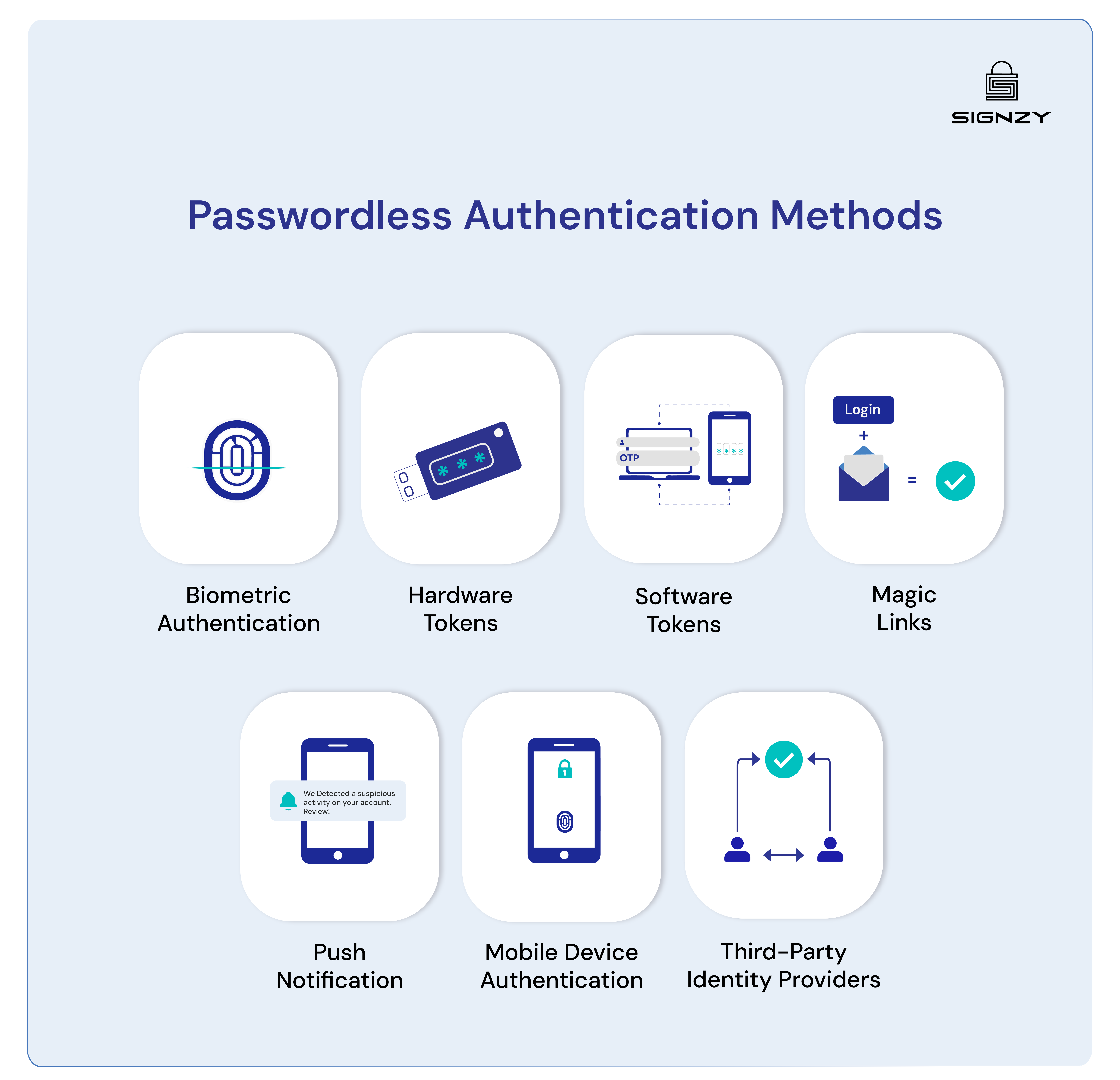
Methods of Passwordless Authentication
Now that you know what passwordless authentication is and its core value, let’s see some available methods.
| Method | How It Works | Advantages | Limitations |
| Biometric Authentication | Scans unique traits (e.g., fingerprint, face, iris), converts them into a secure template and verifies locally. Data stays in a secure enclave, with only tokens shared. | Natural user interaction
Hard to replicate Fast verification Built into devices |
Requires specific hardware
Privacy concerns Backup needed Security of stored data |
| Hardware Tokens | Uses a private key to sign server challenges. Physical presence is required for FIDO2 tokens. The server validates the response using a public key. | High security
Cross-platform Network independent Phishing-resistant |
Physical loss/theft risk
Management overhead Costly distribution |
| Software Tokens | Generates time-sensitive codes (TOTP) via an app using a shared secret and timestamp. The server verifies by generating the same code. | No hardware needed
Cost-effective Easy distribution Broad compatibility |
Device reliance
App setup Sync issues Recovery challenges |
| Magic Links | Sends a temporary, signed URL to the user’s email. Clicking the link verifies both email ownership and token validity. | Familiar
Simple to implement Accessible Low friction |
Email reliability
Time-sensitive Security trade-offs Email access required |
| Push Notifications | Sends a login request to the user’s device. The user approves, and the device signs a challenge using stored credentials for server verification. | Easy to use
Real-time Clear interface Mobile integration |
Network dependency
Alert fatigue Device and battery reliance |
| Mobile Device Authentication | Uses secure hardware (TPM, Secure Enclave) to store keys. Local biometric or PIN verification grants access, and then keys are used for server authentication. | Convenient
Hardware-secured Modern UX Platform integrated |
Device-specific
OS constraints Updates required Recovery hurdles |
| Third-Party Identity Providers | Redirects users to a provider for authentication (OAuth 2.0/OpenID). The provider validates and returns a token to confirm the identity. | Quick setup
Familiar to users Secure Widely adopted |
Provider reliance
Privacy concerns Integration complexity Requires trust |
Some methods allow flexibility as well. For example, using mobile device authentication for regular access while providing hardware tokens for high-security operations creates a balanced approach to security and convenience.
Passwordless Authentication vs. Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication is the most commonly used method. It adds extra verification steps on top of passwords. Think about when you enter a password and then receive a code on your phone – that’s MFA in action. It makes security stronger by requiring multiple proofs of identity.
Passwordless authentication, on the other hand, completely removes passwords from the equation. Instead of adding layers, it replaces the traditional password with more secure methods like biometrics or security keys.
On the user end, MFA typically asks for more steps: enter a password, wait for the code, and enter the code. While this increases security, it can feel cumbersome. Users might experience delays waiting for codes or face issues when they can’t access their phone.
With passwordless systems, users simply use their fingerprint, face, or security key. No codes to enter, no passwords to remember. The process is both more secure and more straightforward.
Both approaches have their importance, but passwordless authentication represents the more modern solution.
Use Cases of Passwordless Authentication
While Passwordless authentication offers broad security benefits, specific scenarios particularly benefit from this approach.
| Use Case | How Passwordless Authentication Helps |
| Identity Verification | Creates a secure digital identity using your device signatures and biometric patterns, eliminating the need for document verification and password management while maintaining the highest level of security. |
| Account Recovery | Streamlines regaining account access through a combination of your trusted devices and biometric markers, removing the traditional friction of security questions and temporary password cycles. |
| Secure Transactions | Enables high-value transaction authorization through multi-factor biometric verification, significantly reducing fraud risks while maintaining a seamless approval process. |
| Cross-Device Access | Enables seamless authentication across all your devices through synchronized cryptographic keys, ensuring consistent access regardless of which device you’re using. |
| Instant Service Access | Facilitates immediate access to time-sensitive services using pre-verified device |
At Signzy, we understand that transitioning to passwordless authentication needs to be smooth and reliable. That’s why our suite of APIs comes with OTP verification, advanced liveness checks, facial matching, and more such capabilities, allowing you to integrate these easily with your existing systems and security measures while providing the user experience modern businesses demand.
FAQs
Can passwordless authentication work offline?
Yes, many passwordless methods like biometrics and security keys work without internet connectivity, using device-based verification.
How does passwordless authentication handle multiple users on shared devices?
Each user maintains their own secure profile and authentication method, with quick switching capabilities similar to password-based systems.
Can passwordless authentication integrate with existing security systems?
Most passwordless solutions offer standard integration capabilities with typical identity providers and security frameworks, enabling gradual adoption.
How does passwordless authentication protect against phishing?
By eliminating shareable credentials and using device-based verification, passwordless methods prevent attackers from intercepting or stealing authentication data.