Triangulation Fraud Explained: How It Works & Prevention Tips
February 13, 2025
7 minutes read
-
- As per Visa’s Chief Risk Officer, merchants face losses between $660 million and $1 billion each month due to triangulation fraud.
- A mix of strong KYC, AI-driven fraud monitoring, AML tracking, escrow payments, and delayed withdrawals makes it difficult for scammers to conduct triangulation fraud.
- In Triangulation fraud, fraudsters just sit in the middle and move stolen money through a real transaction.
Ever notice how magicians never actually cut their assistant in half? The trick works because you’re focused on the wrong part of the stage.
Now, think about financial systems. Just like a magic trick, fraudsters rely on distraction. While everyone’s watching for stolen cards and hacked accounts, fraudsters aren’t breaking anything. They’re simply redirecting where you look. No fake accounts. No suspicious transactions. Just legitimate-looking money flows that quietly bypass every security check you’ve built.
Think about it for a minute. When was the last time your system flagged a transaction with a real buyer, a real product, and a real delivery?
Because that’s exactly how triangulation fraud slips through.
If you want to understand how fraudsters pull it off and what you can do, let’s dive directly in.
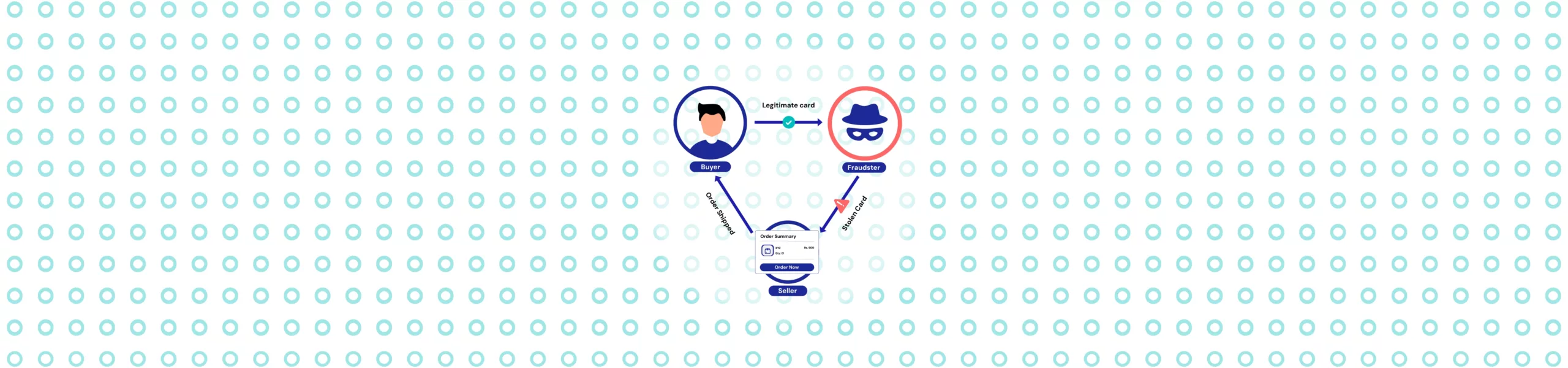
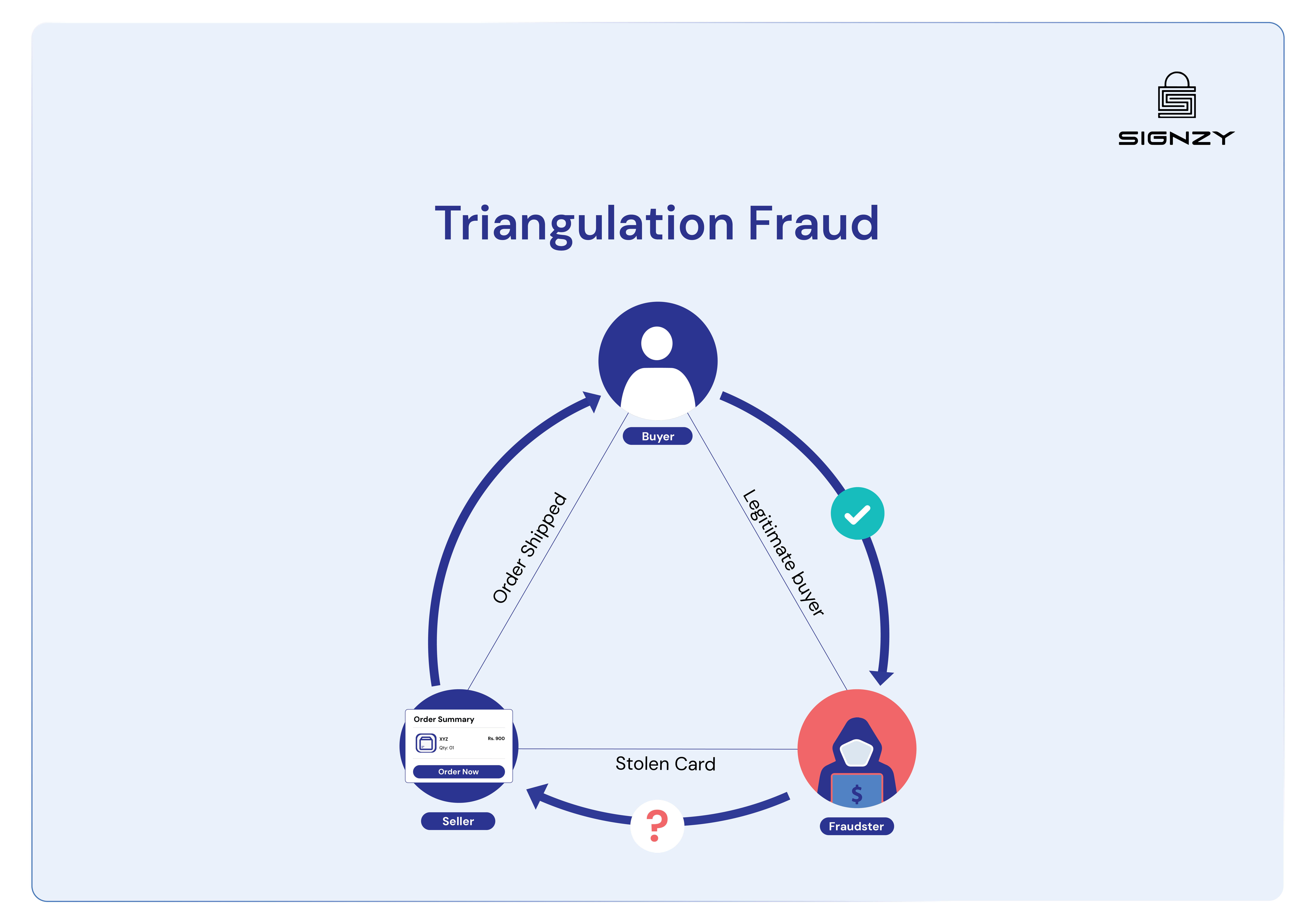
What is Triangulation Fraud?
Triangulation fraud occurs when a scammer acts as a middleman, using stolen credit card information to buy legitimate products and ship them to real customers who unknowingly pay for them.
In this scenario, the fraudster never stocks products or provides services and never directly touches stolen funds. They don’t even get linked to the stolen credentials they’re using.
It usually involves three parties:
- The fraudster (middleman)
- An unsuspecting buyer (customer)
- A legitimate seller (merchant/retailer)
Ultimately, the fraudster pockets clean money, the real cardholder gets hit with a fraudulent charge, and the merchant takes the loss when the fraudulent chargeback comes in.
Triangulation Fraud in Finance: Why It’s a Major Threat?
If you’re running a fintech, neobank, payment processor, lending platform, or any finance-related business, you can be a target of triangulation fraud too.
Fraudsters use weak financial systems to launder money, bypass fraud detection, and exploit chargeback loopholes.
If you don’t clamp down early, your platform could become a fraud highway without you realizing it.
Chargebacks will eat your revenue. Regulators will step in if fraud levels spike. And if fraudsters see your system as easy to abuse, they’ll come in droves.
You need to build barriers now, not after the damage is done.
Before anything else, let’s see how it works so you know what’s exactly going on behind the curtains.
How Does Triangulation Fraud Work?
Triangulation fraud is not some brute-force credit card theft.
It’s a layered, indirect laundering scheme that turns stolen card details into clean, untraceable cash.
Here’s how it works.
1. Setting the Trap
The scammer creates a fake financial service (e.g., investment platform, trading service, or digital banking app) that looks legitimate. Instead of stealing money directly, they use real customer transactions as a disguise for laundering funds. The platform offers attractive but realistic returns to avoid suspicion.
2. Real Customer Invests
A legitimate customer finds the opportunity appealing and deposits money into the scammer’s platform. However, this money isn’t stolen or misused. Instead, the scammer uses this transaction as a cover-up to process fraudulent activity in the next step.
3. Fraudster Places a “Clean” Transaction
Rather than taking the real customer’s funds, the scammer uses stolen payment credentials (hacked credit cards, bank accounts, or PayPal details) to execute the same transaction amount under the customer’s name. This means the financial system sees the legitimate customer as the source of the transaction, not the scammer.
4. Customer Gets Their Return
Since the scammer ensures transactions are completed, the real customer receives their expected payout or investment return. They remain unaware that their name and details have unknowingly been used in a fraud scheme.
Customers are here being used as a “money mule” unknowingly. This eliminates red flags and builds trust.
5. Fraud Alert Hits
Days or weeks later, the real owner of the stolen payment method notices the unauthorized transaction and reports it. The financial institution investigates and traces the fraudulent transaction back to the real customer’s details, not the scammer’s.
6. Fraudster Walks Away Clean
By the time fraud detection kicks in, the scammer has already received real money and shut down their fake platform. Since the fraudulent transaction appears to have come from a real customer, the scammer remains hidden. Tracing them becomes extremely difficult because they never directly handled stolen funds in an identifiable way.
4 Ways to Prevent Triangulation Fraud
1. Make It Harder for Fraudsters to Set Up Accounts (KYC & AML)
Scammers love platforms that let them sign up with zero hassle. If you make it too easy, you’re inviting them in. It requires legitimate business verification, not just an email and phone number.
Enforce strict KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks. This means ID verification, proof of address, and business registration for merchants. If someone is sketchy about proving who they are, that’s a red flag.
Also, don’t let brand-new accounts move money instantly. Hold payouts for at least a week. Real businesses won’t mind waiting, but fraudsters? They’ll bail because they can’t afford delays.
Watch for red flags like fake IDs, mismatched business details, and accounts that barely pass minimum verification standards. These are often fraudsters trying to get in.
2. Block Stolen Cards Before They Get Used
Scammers test stolen cards by making tiny transactions first. Stop that, and you block them before they can even get started. Set limits on repeated small purchases and require extra verification for anything that looks off.
AML risk screening should also apply to payment sources. If a customer is using cards tied to multiple different countries or frequently failing card authorizations, that’s a red flag. Combine this with 3D Secure (3DS) authentication, as it forces buyers to confirm payments with their bank, making it much harder for fraudsters to push transactions through.
3. Watch for Suspicious Marketplace & P2P Activity (AML Monitoring)
Marketplaces and peer-to-peer payments are like playgrounds for scammers. If someone is getting a bunch of random payments from different users out of nowhere, they’re probably laundering money.
A simple fix? Escrow payments.
Hold the cash until the buyer confirms they got what they paid for. AML monitoring should track money flows. If a new account suddenly moves large amounts across multiple small transactions (known as structuring or smurfing), it could be an attempt to launder stolen money.
Freeze withdrawals and ask some questions. If it’s legit, no problem. If not, you just saved yourself a mess.
4. Stop Crypto & BNPL from Becoming a Fraud Magnet
BNPL (Buy Now, Pay Later) is a dream for fraudsters. They use stolen details to max out purchases, then vanish before payments are due. If a brand-new account instantly spends the max limit, hit pause and verify.
Run enhanced due diligence on users requesting high BNPL limits. Fraudsters won’t have a strong credit history, and a deeper review can weed them out.
Crypto is another favorite. Scammers deposit stolen money, swap it for crypto, and send it off before you notice. If a user cashes out too fast, flag it. Use blockchain AML tools like Chainalysis or TRM Labs to track stolen funds. Delaying withdrawals for new users also helps prevent fraudsters from cashing out instantly.
Using Tech to Prevent Triangulation Fraud
Tech is the smart way to block fraud without slowing down legitimate users.
Fraudsters thrive on platforms that skip identity checks or don’t track suspicious activity. With real-time verification and AI-driven tools, you can catch shady behavior before it causes damage.
Here are some examples of how technology can help you prevent triangulation fraud:
- Liveness Check API: Confirms the user is real and physically present, blocking fraudsters using fake or stolen documents.
- Face Match API: Matches live selfies with ID photos instantly, ensuring users are who they claim to be.
- PEP Screening API: Flags high-risk users by scanning global watchlists, keeping your platform safe and compliant.
To learn more about keeping your platform fraud-free, click here.
FAQs
Why should fintechs care about triangulation fraud?
Fraudsters use weak KYC/AML processes to move stolen funds through BNPL, crypto, or payment platforms. If unchecked, chargebacks and regulatory issues pile up fast.
How does KYC help prevent triangulation fraud?
KYC verifies user identities, making it harder for scammers to set up fake accounts. Stronger checks like ID verification, video KYC, and business registration prevent fraudsters from easily onboarding.
What role does AML play in stopping this fraud?
AML tracks suspicious money movements, like structuring or layering. It flags accounts trying to cycle stolen funds through multiple small transactions to clean them.
How do I detect if my platform is being used for triangulation fraud?
Look for patterns—new accounts receiving high payments, mismatched billing/shipping, rapid spending sprees, or frequent chargebacks. AI-driven fraud detection helps spot these red flags.