Due to advancements in technology and the accessibility of fund transfers, risks of money laundering and terrorist financing are on the rise!
Understanding AML Risks
Though the global financial system was aimed at convenience, it is now exposed to great risk. Criminal-minded people are taking this complicated system to transfer funds illegally overseas without getting caught.
As the need to whitewash shaded wealth (money derived from tax evasion, corruption, drug trafficking, etc.) arises, financial frauds proliferate.
Injecting funds obtained through these crimes into the legal financial system gives birth to Money Laundering.
To mitigate these risks, a financial organisation needs to establish a robust Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Program.
This program provides insurance coverage against money laundering for the organisation.
How?
By streamlining corporate operations with regulatory compliances.
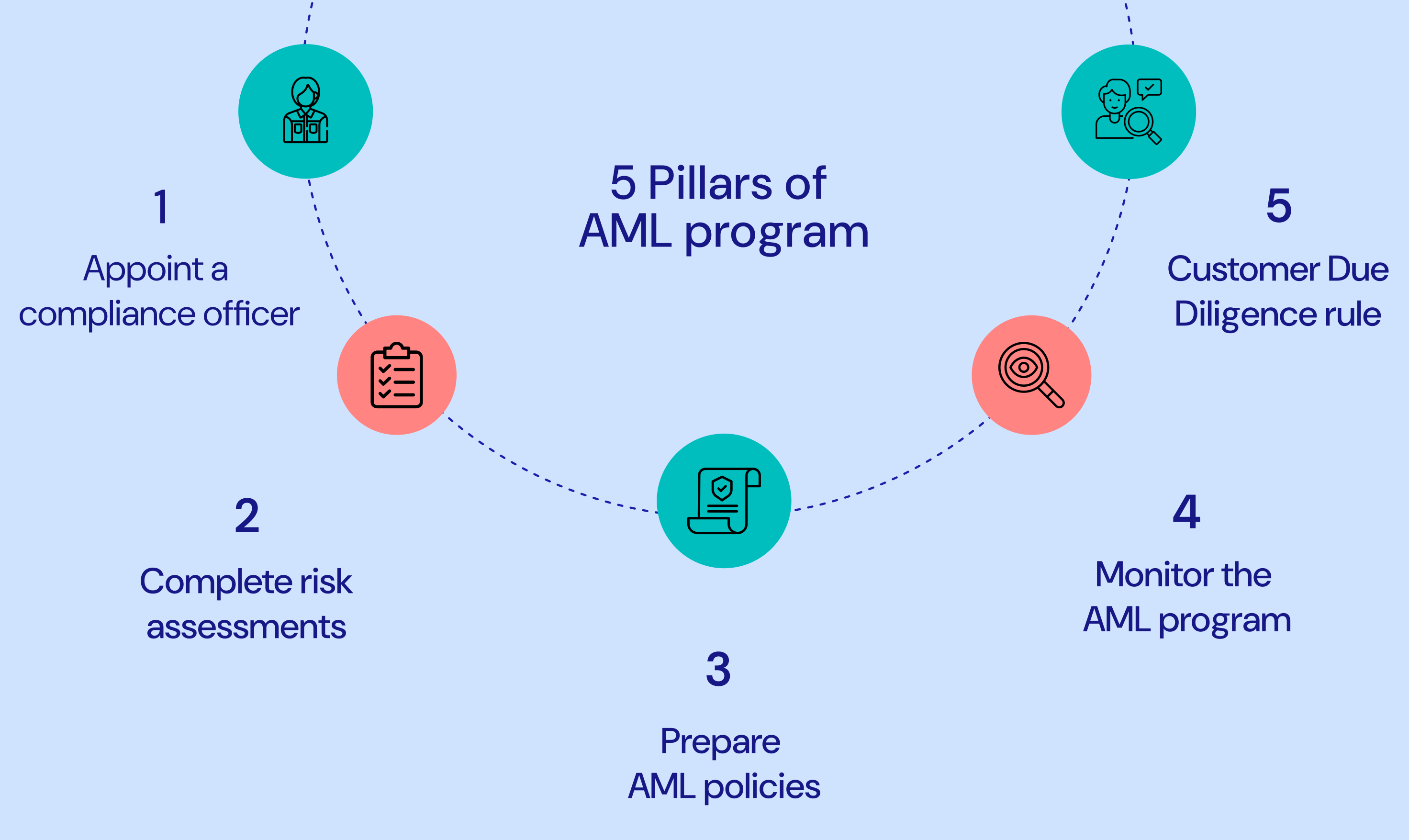
As per the Bank Secrecy Act, the foundation of an AML compliance framework needs to be laid upon five pillars:
- Appointment of a compliance officer
- Completion of risk assessment procedures
- Preparation of anti-money laundering policies
- Continuous monitoring of such policies and programs
- Implementation of customer due diligence (CDD)
What’s the purpose of AML pillars?
The purpose of these pillars is to:
-Provide a systematic and thorough approach to compliance.
-To focus extensively on internal controls, assigned responsibilities, and employee training
-To strengthen by eliminating potential gaps
Now, let’s comprehend these pillars in detail.
#1. Appoint a compliance officer
It is essential to appoint a designated compliance officer (also known as Money Laundering Reporting Officer or MLRO).
What are his responsibilities?
-To ensure the effectiveness of the organisation’s AML efforts
-To ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations
-To ensure plausible communication with the regulatory authorities
An MLRO or compliance officer coordinates with different functions within the organisation to implement and maintain the AML programme smoothly. The Compliance Officer must possess the necessary expertise and be given appropriate authority.
Other responsibilities include communicating with auditors, briefing upper management, and making AML policy suggestions based on audit findings and continuous assessments.
An AML Compliance Officer’s knowledge should not be confined to just the legal compliances. Rather should extend to the detailings of the financial crimes for complete discovery and reporting.
MLRO must be ART compliant – Authority, Resources, and Training – all of which should be as per the business’s risk.
#2. Complete risk assessments
Robust internal controls, well-defined protocols, and clearly outlined procedures make an AML compliance program robust.
Measures such as verification of the identity of customers and reporting of any unusual transactions to the relevant authority must be in place. Strong internal controls in an organisation lead to fewer violations of laws and regulations.
Risk-based approach must be followed in the organisations – mitigation measures depend upon the level of risk. Therefore, risk assessments cannot be static. The controls should be frequently reviewed and updated so that changes in the business operations, regulatory landscape, and exposed risks can be taken into consideration.
#3. Prepare anti-money laundering policies
It is important to constitute a dedicated team for compliance in the organisation.
Why?
To effectively manage and address risks.
How?
By keeping an eye on evolving industry trends and new compliance requirements.
An organisation’s best weapon to fight against the risks of money laundering is a well-trained and informed workforce. AML training is crucial not only for positions prone to high risk but for all employees.
Training must relate to the tools and technologies for fraud detection and should be focused on the protocols for disclosing fraudulent activities.
Training is an ongoing process; frequent trainings are required whenever any change or modification is made to your AML compliance program.
Identification of suspicious activity, reporting responsibilities, and the repercussions of non-compliance should form part of the training of training program.
Through vigilance, employees can be encouraged to identify and report suspected activities promptly.
#4. Monitor and maintain your AML program
Routine testing and frequent audits of the organisation’s AML program validate the performance of the program.
Review from external sources ensures
the adequacy of your internal controls,
the effectiveness of AML policies and procedures, and
the compliance of applicable laws and regulations.
For any identified gaps or flaws during the review, corrective actions need to be taken, and that too quickly.
These reviews are essential to uphold operational integrity.
It is important to know that compliance audits are not the same as financial audits. They are different. Compliance audit focuses only on the AML requirements and the organisation’s attempts to protect itself from any illegal activity.
Such an audit is essential for pinpointing flaws, improvising procedures, and verifying conformity with legal requirements.
#5. Implement Customer Due Diligence
CDD rule i.e. Customer Due Diligence rule was introduced in May 2018 by Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
Today, it is one of the five fundamental pillars of the AML compliance program.
What’s the CDD rule?
Mandates organisations to check and verify their customer’s identity and to observe closely their affairs and dealings in order to spot and report any questionable transactions.
The following four core elements must be taken care of while carrying out CDD:
- Confirming the identity of customers and determining their degree of risk
- Identifying the ultimate beneficiaries of legal entities
- Maintaining good relationships with the clients
- Monitoring transactions to flag any unusual behaviours or trends
The CDD rule is based upon the risk game, where organisations need to evaluate both the clients and transaction requests based on their level of risk.
Due diligence procedures must be tailored as per the risk associated with each customer and transaction. Also, enhanced due diligence (EDD) measures must be implemented, wherever necessary, like in the case of transactions made by clients who pose a greater risk.
Risks associated with money laundering differ based on the nature of clients, products, services, and participating nations. By using a risk-based approach to Customer Due Diligence, your organisation can deploy resources efficiently and shift its complete focus to such areas where there are high chances of fraud.
A successful AML program needs continuous awareness and improvement, and agility to keep up with changing laws and regulations to stay ahead of flourishing threats in this dynamic landscape of financial crimes.
Stay AML Compliant with Signzy
If putting the five AML pillars into practice, keeping an eye on transactions, filing reports, performing frequent audits, or training new hires in one sitting seems like too much of a hassle…
Then it would be best if you consider implementing Signzy’s API, a complete game-changer for you.
The API offers a powerful tool to help organisations improve their AML measures. By leveraging this API, real-time data breach information can be fetched into the system. This facility can help organisations to detect weaknesses and implement proactive methods to strengthen their security measures.
So, if you need guidance on building an effective AML compliance program, our identity verification procedures, AML screening, risk-scoring, and other solutions can assist you to transform and streamline your compliance workflow.
Visit our website for more information!