What is biometric verification? Step-by-step process for businesses: Methods, examples, pros and cons
- An NFC chip’s encrypted communication happens in microseconds, yet it’s complex enough that breaking its security would take a supercomputer several hundred years.
- A single NFC verification contains more security checkpoints than an entire airport screening process from the 1990s, all completed in under 2 seconds.
- 90% of smartphones now come with NFC capabilities pre-installed, meaning businesses can implement NFC solutions without asking customers to acquire new hardware.
Imagine you’re at a big family reunion.
There are a lot of faces—relatives you don’t see often, so recognizing them takes effort. But when you spot your mom across the room, you don’t even have to think about it—you instantly know it’s her without checking ID or asking questions.
Your brain just does it.
That’s exactly what biometric verification offers: the ability to instantly identify someone – by their face, fingerprint, voice, or other biological features digitally – but at a business scale, with a speed and precision that human intuition can’t match.
Although, like any technology, biometrics has its pros and cons, it offers a level of security that’s much harder for hackers to crack.
For example, fingerprints have 150 unique points, facial recognition relies on 80 nodal points, and iris scans use 240 distinct identifiers—making it far more difficult to compromise than an 8-10 character password.
If you are looking to create a secure, frictionless experience for your users that works in the background, letting you focus on running your business while security takes care of itself – this guide is worth your next 6 minutes (read time).
Related Solutions
What is Biometric Verification?
Biometric verification is an automated method of verifying a person’s identity using their unique biological and behavioral characteristics.
Think of it as a sophisticated digital system that turns bodily features into secure authentication keys – but far more complex than traditional passwords or PINs.
The process works through an integrated technology stack:
| Collection Layer | High-precision sensors capture biometric data (facial features, fingerprints, voice patterns) Quality control ensures optimal data capture Initial encryption begins at the point of capture |
|---|---|
| Processing Core | AI algorithms convert biological traits into digital templates Matching engines compare live samples against stored templates Advanced fraud detection systems screen for spoofing attempts |
| Security Architecture | Encrypted databases store biometric templates (not actual images) Secure transmission protocols protect data in transit Compliance frameworks ensure data protection (NIST standards, ISO requirements) |
Common Biometric Methods & Implementations
When it comes to biometric verification methods, businesses today have several powerful options. Let’s explore the most effective ones.

1. Facial recognition
The method analyzes 80 unique points on a person’s face, making it extremely difficult to fool. For businesses handling remote customer verification, it’s particularly valuable because it works seamlessly through everyday devices like smartphones.
Imagine your customer simply taking a selfie to securely access their account or complete a high-value transaction – that’s the convenience facial recognition offers.
2. Fingerprint scanning
Fingerprint scanning is a time-tested method. The technology has evolved significantly from its early days:
- Captures 150 unique comparison points for accuracy
- Works instantly through mobile device sensors
- Ideal for both physical access control and digital authentication
- Particularly effective for employee verification systems
3. Voice recognition
Think about how natural it feels for customers to verify their identity just by speaking – no passwords to remember, no codes to enter.
However, businesses should note that 37% have experienced deepfake attempts, making it crucial to use voice verification as part of a multi-factor approach rather than standalone.
4. Iris scanning
For organizations requiring the highest level of security, iris scanning provides unmatched accuracy with its 240 distinct identifiers. While it requires specialized equipment, making it less suitable for remote verification, it’s becoming increasingly popular in:
- Government facilities
- Financial institutions
- Healthcare settings
- Border control systems
Many organizations find that combining multiple methods provides the optimal balance of security and convenience.
💡 Related Blog:
Implementation Guide for Businesses
Successfully implementing biometric verification doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here’s your step-by-step roadmap to get it right:
Step 0 – Start With the Right Questions
Before diving into vendor catalogs, take a step back. Ask yourself:
- What’s your biggest authentication headache right now?
- Are you losing customers during verification?
- How many verifications do you handle daily?
- What’s your fraud loss in the last year?
- What does compliance say in your region?
These answers will help you throughout the implementation. For instance, if you’re seeing high dropout rates during customer onboarding, you might want to prioritize facial verification for its ease of use. If fraud is your nightmare, a multi-modal approach might be your best bet.
Step 1 – Smart Vendor Selection
Think of choosing a vendor, like hiring a key team member. You need someone who:
- Speaks your industry’s language
- Has battled similar challenges
- Offers support when things get tough
- Won’t break your bank
Don’t just look at fancy demos. Ask for a pilot program. Nothing beats real-world testing with your actual users.
Step 2 – Implementation
Here’s an approach that won’t disrupt your operations:
Begin with your friendly MVPs – a small group of 100-500 users who can help you perfect your game plan. These early adopters can help you provide insights into what is working and what is not. You just can’t get that from a test environment. Their experience will help you smooth out any rough edges before going mainstream.
Track these crucial early signals:
- How long are verifications taking?
- Where are users getting stuck?
- What’s making them smile vs. sigh?
These signals tell you exactly what needs fixing before it becomes a bigger issue.
Once your pilot group is sailing through verifications with minimal hiccups, you’re ready to expand. Also, expand in waves, not tsunamis. Each new user group brings its own challenges and insights.
Keep your ear to the ground and your hand on the pulse – when verification success rates hit above 95% and user complaints are minimal, you’ll know you’re on the right track.
Step 3 – Tracking Metrics and Iterating
Don’t drown in data. Focus on what matters:
- Are verifications happening in under 30 seconds?
- Is fraud going down?
- Are customers sticking around?
Don’t wait for long in any phase – perfect is the enemy of good. Start somewhere, measure what matters, and keep improving.
Pros and Cons
It’s not all sunshine and rainbows. Here’s a good look at the advantages and challenges.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Reduces fraud | High initial implementation costs ($50K-$200K) |
| Eliminates password management overhead | Requires robust backup authentication systems |
| Provides clear audit trails for compliance | Complex privacy regulations by state |
| Cuts verification time to seconds | Technical infrastructure requirements |
| Enables seamless omnichannel experience | Environmental factors can affect accuracy |
| Reduces operational costs long-term | Integration challenges with legacy systems |
| Enhances regulatory compliance | Staff training and change management needs |
| Improves customer satisfaction scores | Data storage and protection costs |
| Enables secure remote transactions | Regular system updates and maintenance |
| Scalable across multiple channels | User enrollment and education process |
| Reduces customer support burden | Network dependency |
| Future-proof authentication method | Potential accessibility issues |
For most businesses, the pros far outweigh the cons – but success lies in going in with eyes wide open and a solid game plan.
Biometric Verification Security Example
Let’s examine how Binance, the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange, leverages biometric verification to set new standards in digital asset security:
To combat the rising threat of identity fraud in crypto trading, Binance implemented a comprehensive biometric verification system that’s now considered a benchmark in the industry.
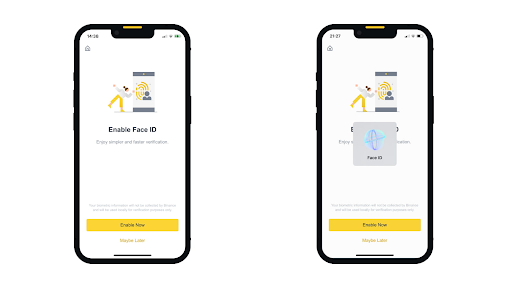
The process starts with mandatory face verification during signup – users simply take a photo of their ID and a selfie, which are then matched using advanced algorithms.
They’ve cleverly added liveness detection as their second security layer.
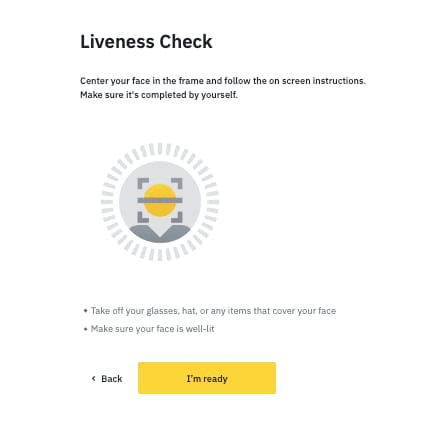
Instead of just accepting a static selfie, the system asks users to perform random actions like blinking or turning their heads – a simple yet effective way to catch fraudsters trying to use photos or deepfake videos.
For high-stakes moments – like large withdrawals or security setting changes – Binance adds an extra verification step. Just like how a bank might ask for additional ID for significant transactions, but here it’s as simple as a quick face scan.
Stop fraud at the first step. Signzy’s AI-powered biometric stack combines real-time face matching with advanced liveness checks, processing millions of verifications daily. Used by leading banks and fintechs across 200+ countries, our solution delivers secure verification in under 30 seconds. Ready to upgrade your security? Let’s talk.
FAQ
Is biometric verification more secure than traditional passwords?
What happens if my biometric data is stolen?
What if the biometric system fails to recognize a legitimate user?
Do I need to worry about privacy regulations when implementing biometric verification?

Gaurav Gupta
Gaurav Gupta is the Global Product Head at Signzy, leading the strategy and development of the company’s KYC, KYB, AML, and digital onboarding products used by banks, fintechs, and financial institutions across global markets. He specializes in building scalable compliance and verification platforms, transforming complex regulatory and risk workflows into seamless, automated product experiences. Gaurav works at the intersection of product, engineering, and AI.




![Complete Guide to Biometric Verification Systems for Businesses [2025]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/blrzl70g/production/9a1c9d59369092cec352be3cb9a46f25e54457e1-2821x663.png)
![Common Uses of Biometrics in Business [Examples Included]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/blrzl70g/production/4de0ced79be899652dd0b149acbf195bb67e5a63-2821x663.png)

