- An NFC chip’s encrypted communication happens in microseconds, yet it’s complex enough that breaking its security would take a supercomputer several hundred years.
- A single NFC verification contains more security checkpoints than an entire airport screening process from the 1990s, all completed in under 2 seconds.
- 90% of smartphones now come with NFC capabilities pre-installed, meaning businesses can implement NFC solutions without asking customers to acquire new hardware.
Today, you probably wave your phone or card dozens of times daily without thinking twice about the invisible technology making it happen. This simple act of waving a device to make something happen is powered by Near Field Communication (NFC).
Think of it as a tiny radio conversation happening between two devices when they get close enough to ‘whisper’ to each other. But this simple ‘whisper’ involves more security protocols than the entire banking system of the 1980s.
And now, these ‘whispers’ can become your strongest identity verification tool.
You’re about to learn exactly what this means for your business, what compliance checks you need, and how to implement them properly.
Ready to make most of your next 7 minutes?
It starts now.
What is NFC?
Near Field Communication represents a practical advancement in secure data exchange technology. If you’re running a business, you’ll appreciate that an NFC chip simply works – creating protected data transmission between devices placed within centimeters of each other.
Unlike Bluetooth or Wi-Fi that broadcast across rooms, NFC’s limited range makes it naturally secure for sensitive operations.
The technology relies on two key components: an NFC chip (the tag) and a reader. The reader activates the chip using electromagnetic waves, creating a secure, two-way conversation for data exchange. This simple yet sophisticated setup powers everything from contactless payments to identity verification.
Here’s what makes this relevant now: 90% of smartphones include NFC capabilities, and the supporting infrastructure is solid across the US market. Since people already use this technology for payments, adopting it for verification feels natural to most users.
💡 Related Blog: What is Identity Verification?
Business Case for NFC
Let’s talk about what NFC really means for your business operations. We know security and efficiency matter to you – and that’s exactly where NFC shows its worth.
Think about your current verification process. How much time does your team spend checking documents? How often do you worry about potential fraud?
NFC in verification changes this completely.
Each NFC chip contains encrypted data that’s extremely difficult to alter, making every NFC check reliable. While traditional document verification becomes more vulnerable to sophisticated forgery, NFC provides consistent security.
The practical benefits are clear in daily operations. Rather than spending minutes on manual document checks, verification happens with a simple tap.
That’s time and money you can invest back into growing your business. Key uses worth noting are:
- Immediate authentication of identity documents: Documents are verified instantly as NFC chips contain digitally signed data that can’t be copied or altered, unlike traditional paper documents.
- Protection against document tampering: Each NFC chip’s encrypted structure makes modification practically impossible – any attempt to tamper breaks the chip’s digital signature.
- Automated data capture with excellent accuracy: Direct digital transmission eliminates human error in data entry, while ensuring all required fields are captured completely.
- Notable reduction in operational costs: By removing manual verification steps and reducing fraud-related losses, businesses save on both time and verification resources.
Most importantly – your customers will thank you too.
Instead of the frustration of uploading documents or waiting for manual verification, they simply tap their ID against a device – the same motion they’re comfortable with from making payments.
Trade-offs
While NFC technology offers compelling benefits, making an informed decision requires weighing both its strengths and limitations.
And if we are telling what’s good, we won’t hide ugly. Here’s a comprehensive look at what NFC means for your operations:
| Advantages | Limitations |
| Strong Security – Tamper-proof chips with sophisticated encryption | Device Requirements – Needs NFC-enabled devices for operation |
| Efficient Data Transfer – Error-free data transmission | Limited Range – Only works within 4cm distance |
| Enhanced User Experience – Simple tap interaction | Access Restrictions – Some data only readable by authorities |
| Quick Verification – Instant document authentication | Implementation Costs – Initial infrastructure investment needed |
| Automated Data Entry – Eliminates manual input errors | Market Coverage – Not all regions have NFC-enabled IDs |
| Real-time Authentication – Immediate validation results | Technical Barriers – Budget phones may lack NFC capability |
| Contactless Operation – No physical contact needed | User Familiarity – Some customers may need guidance |
From the above table, if pros outweigh cons for your business, the next section is for you.
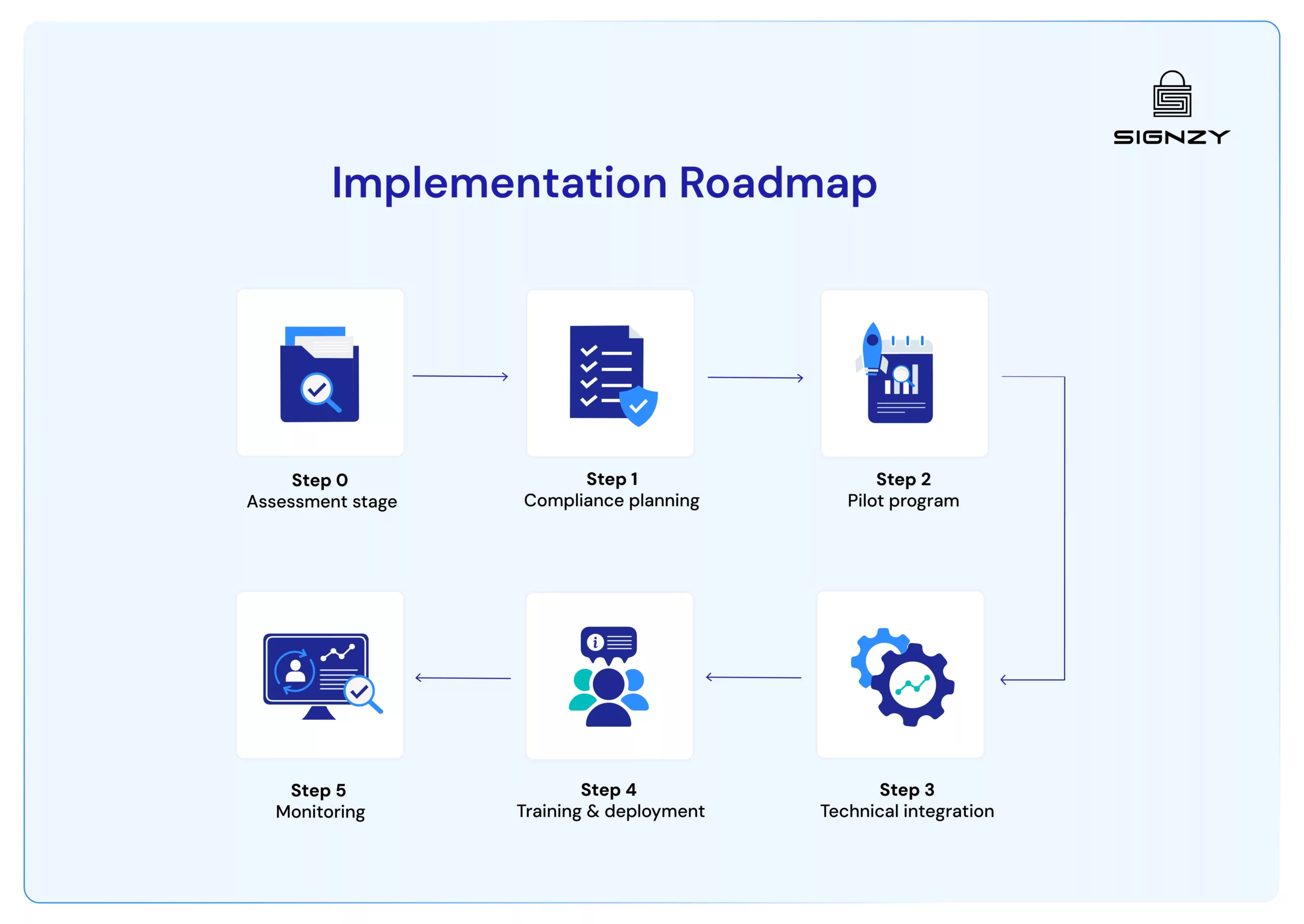
Implementation Roadmap
Adding NFC technology to your business might seem complex, but it doesn’t have to be. We’ll break it down into manageable steps.
Step 0 – Assessment stage
Look at what you already have. Most current systems work well with NFC verification solutions. You’ll need secure data processing capabilities and API integration points. This evaluation helps identify any technical gaps before you invest.
The goal should be building on your current strengths while addressing potential weaknesses.
Step 1 – Compliance planning
Your NFC system must meet several regulatory requirements. Work with your compliance team to address:
- AML compliance standards
- KYC protocol requirements
- Data protection regulations
- Industry-specific requirements
- Cross-border rules (for international operations)
Pro tip: Create a compliance checklist. It helps track requirements and serves as documentation for audits.
Step 2 – Pilot program
Smart implementation starts small. Choose a specific department or customer segment for your pilot program. This controlled environment lets you test the system thoroughly and gather valuable feedback. Your team can learn the new processes without pressure, and you’ll spot potential improvements before scaling up.
Step 3 – Technical integration
Here’s where planning turns into action. Working with your technology team or provider, set up:
- NFC-enabled verification devices
- Secure data processing systems
- Integration with existing customer databases
- Backup verification methods for exceptional cases
Step 4 – Training and deployment
Your team’s confidence with NFC technology directly impacts customer experience. Develop a clear training program that covers both technical operation and customer communication. Show your staff how NFC checks improve their daily work – when they see the benefits, they’ll become natural advocates for the system.
Step 5 – Monitoring
Once your NFC system is running, watch it closely. Track verification speeds, success rates, and customer feedback. This data helps you fine-tune the system and proves its value to your business.
Strategic Applications of NFC
NFC technology has proven its worth across multiple business functions, with real impacts on security and efficiency.
-
Identity verification & security
The security comes from the NFC chip’s encrypted data structure – each chip contains digitally signed information that provides reliable, instant authentication. This has become particularly important as traditional document verification faces increasing fraud risks.
- Access control systems
The application of NFC extends beyond basic verification:
- Facility access management
- Smart lock systems
- Virtual business cards
- Document authentication
These systems benefit from NFC’s inherent security features, as the short-range communication (within 4 cm) makes unauthorized interception extremely difficult.
-
Customer engagement & transactions
According to ICAO data, over 140 countries now issue electronic passports with NFC capabilities. This widespread adoption has led to increasing integration across industries:
- Banking sector identity verification
- Transport ticketing systems
- Retail payment systems
- Cross-border identification
Making NFC Work For Your Business
While NFC technology’s benefits are clear, your implementation success depends on having the right technology foundation. When you’re evaluating solutions, look for platforms like Signzy that combine NFC checks with comprehensive verification systems.
You’ll want a system that handles validations quickly (ideally under 30 seconds), works across multiple countries, and integrates additional security measures like liveness checks, face match and more. This multi-layered approach ensures you get the full value of NFC technology while keeping your verification process streamlined and secure.
Curious about implementation costs and timelines? Our team is here to help – schedule a no-obligation call today.
FAQs
Does NFC verification work if my customer's phone has no internet connection?
Yes. NFC operates independently of internet connectivity. The verification happens directly between the ID document’s chip and the reading device through close-range electromagnetic waves.
How secure is NFC compared to traditional document scanning?
NFC offers higher security as it reads encrypted data directly from the chip, which cannot be photocopied or manipulated like physical documents. Each verification also creates a unique encrypted session.
What types of ID documents typically have NFC chips?
Most modern passports, national ID cards, and some driver’s licenses contain NFC chips. Over 140 countries now issue electronic passports with NFC capabilities.
Do I need special hardware to implement NFC verification?
Most modern smartphones (post-2019) can handle NFC verification. For business implementation, you mainly need NFC-enabled phones or tablets and the appropriate verification software.