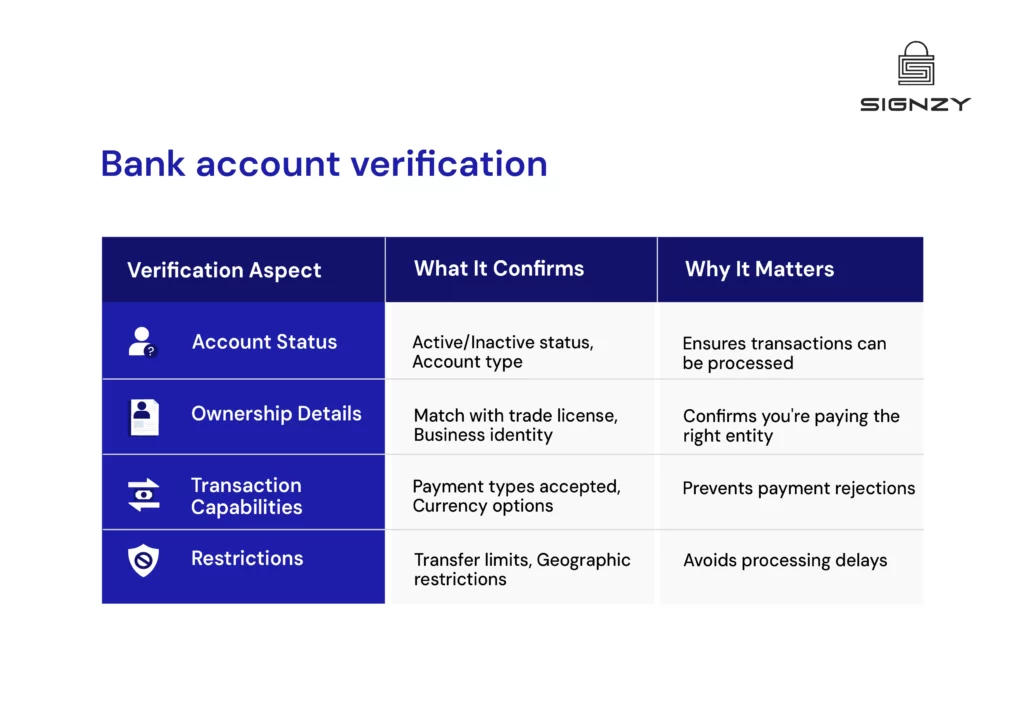
- Many profitable UAE companies face bank account rejection despite healthy financials – institutional compliance outweighs business metrics.
- Most UAE banks require minimum balances ranging from AED 25,000 to AED 1,000,000 for corporate accounts – choosing the right bank makes a significant difference.
- Free zone companies enjoy different banking privileges compared to mainland businesses, affecting account opening success rates.
No grand statements about Dubai’s banking landscape. No impressive statistics about digital payments. Below is just a clear breakdown of what you actually need to know about opening a business bank account in the UAE.
Grab a coffee (make it extra hot!) – in the time it takes to drink it, you’ll understand the entire account opening process inside out.
Prerequisites for Opening a Corporate Bank Account in UAE
The foundation for opening a corporate bank account begins with having a properly registered business entity in the UAE.
The UAE Commercial Companies Law stipulates specific requirements for different business structures.
Key prerequisites include:
- Valid trade license from relevant authorities (DED for mainland, respective authorities for free zones)
- Physical office space with authenticated lease agreement/Ejari
- Minimum capital requirements (varying by bank and business type)
- UAE residency visa for at least one shareholder/director
- Initial deposit amounts ranging from AED 10,000 to AED 50,000
UAE Business Bank Account Application Process
1. Bank Selection and Initial Contact
The UAE’s banking landscape comprises both local powerhouses and established international institutions. Local banks like Emirates NBD, with over 300 branches in Dubai alone, offer extensive regional networks and competitive local transaction rates.
Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank provides five distinct account options with minimum balance requirements from AED 25,000 to AED 1,000,000, while Mashreq Bank offers specialized business packages starting at AED 25,000 minimum balance.
Schedule a preliminary consultation with bank of your choice, where relationship managers will assess:
- Business structure, activities, and revenue model
- Expected monthly transaction volumes and banking patterns
2. Documentation Submission
After the initial consultation, submit a complete documentation package including trade license, incorporation documents and other important documents to the bank. Here is full list of documents you must have:
| Document Category | Mainland Companies | Free Zone Companies | Foreign Entities |
| Core Company Documents | – Trade License
– Memorandum of Association (MoA) / Articles of Association (AoA) – Share Certificates – Commercial Registration |
– Free Zone License
– Share Certificate – Free Zone Registration |
– Parent Company Registration
– Certificate of Incorporation – Board Resolution Authorizing UAE Activities |
| Personal Documents | – Passport Copies
– UAE Residency Visa – Emirates ID – Residential Address Proof |
– Passport Copies
– UAE Residency Visa (if applicable) – Emirates ID |
– Passport Copies
– Home Country ID – Proof of Residential Address |
| Business Verification | – 6 Months Bank Statements
– Office Lease / Ejari Registration – Utility Bills |
– Free Zone Office Lease / Contract
– Bank Statements – Business Activity Report |
– Parent Company Bank Statements
– Certificate of Good Standing (if applicable) – Company Profile |
| Additional Requirements | – VAT Registration (if applicable)
– Details of Trade Partners / Business Partners – Source of Funds Declaration |
– Free Zone Activity Permit
– No Objection Certificate (NOC) from Free Zone Authority |
– Apostilled or Attested Documents
– UAE Agent Agreement (if applicable) – Source of Funds Declaration |
According to the UAE Banking Federation, document authenticity verification typically takes 2-4 weeks, though this timeline can extend based on the complexity of the business structure and the completeness of submitted documentation.
For foreign entities, documents must be attested by the UAE Embassy in the country of origin and the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs, a process that can cost approximately AED 2,000 per document.
A dedicated bank officer reviews this package for completeness before forwarding it to various departments.
3. Enhanced Due Diligence
Banks conduct thorough background checks on the company and its shareholders. This includes verifying trade references, analyzing ownership structures, and assessing industry-specific risks. For high-risk sectors like cryptocurrency, digital assets, fintech, money services, or precious metals trading, banks perform additional scrutiny including regulatory clearances and specialized licenses.
The compliance team examines source of funds documentation with particular attention to international transfers and cross-border transactions. Companies dealing with cryptocurrencies or digital assets must provide clear transaction trails and regulatory compliance proofs. The bank may request additional documentation showing Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures, transaction monitoring systems, and risk management protocols.
High-risk industries also need to demonstrate:
- Detailed operational procedures and internal controls
- Compliance with UAE Central Bank’s regulatory framework
- Clear audit trails for all major transactions
For fintech companies, gaming businesses, or investment firms, banks require proof of relevant regulatory approvals from authorities like the UAE Central Bank, SCA (Securities and Commodities Authority), or specific free zone regulators. The due diligence process for these sectors typically extends beyond the standard 2-4 week timeline.
4. Face-to-Face Interview
A mandatory meeting with bank officials follows successful document verification. Company shareholders or authorized signatories must attend this meeting personally.
The discussion covers operational details, expected banking patterns, and specific service requirements. Banks typically require clarity on:
- Monthly transaction values (estimates)
- Frequencies of transactions (estimates)
- Major trading partners
- Payment corridors
5. Committee Review and Approval
The bank’s internal committees evaluate the complete application. This process typically takes 7-10 working days.
For approved applications, the bank issues formal account opening agreements and fee schedules. Review these documents carefully as they outline important terms including transaction limits and charges.
6. Account Activation
Upon approval, complete these final steps:
- Sign all account opening documents in person
- Deposit the minimum balance requirement
- Complete biometric verification for authorized signatories
- Receive account credentials and online banking access
- Set up digital banking services and security protocols
7. Post-Activation Setup
Within the first month of operation, establish essential banking services:
- Register for payment processing systems
- Set up standing instructions if needed
- Configure transaction alerts and notifications
- Schedule initial meeting with assigned relationship manager
The entire process, from initial consultation to account activation, typically takes 2-4 weeks for straightforward applications. Complex structures or regulated industries may require additional time for enhanced due diligence.
Accelerating Banking Operations
Establishing a corporate bank account in the UAE marks just the beginning of your banking journey. Businesses require ongoing compliance monitoring, regular KYC (Know Your Customer) & KYB (Know Your Business) updates, and thorough transaction screening – particularly crucial for businesses in regulated sectors or those handling international transfers.
Modern verification technology offers a strategic advantage in meeting these extensive requirements. Organizations can automate critical compliance processes, transform multi-week verifications into same-day clearances, and maintain continuous monitoring without expanding internal resources.
As manual processes become increasingly time-consuming, businesses are turning to automated solutions. Signzy supports this transition with proven tools like Business Verification API, UBO Checks, and Document Authentication – helping organizations simplify their banking operations while maintaining strong compliance standards. Make your banking operations more efficient today.
Streamline your verification processes with our automated solutions – Explore our verification APIs.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long does the corporate bank account opening process typically take in the UAE?
A: Standard applications take 2-4 weeks from initial consultation to account activation. Complex structures or regulated industries may require additional time due to enhanced due diligence.
- What are the minimum balance requirements for corporate accounts?
A: Requirements vary by bank – ranging from AED 25,000 to AED 150,000 for standard business accounts. International banks typically require higher minimums than local banks.
- Do all shareholders need UAE residency for opening a corporate account?
A: At least one shareholder or director must have UAE residency. Some international banks offer more flexibility, especially for established foreign companies.
4: Are there additional requirements for fintech and digital asset companies?
A: Yes. These sectors require additional regulatory approvals, enhanced compliance documentation, and specialized licenses from UAE Central Bank or relevant free zone authorities.