The base for data privacy and protection is crucial for an upcoming data-driven economy like India. India hosts almost 450 million Internet users and a consistent growth rate of 7–8%, as per Forbes. The transition to a digital economy is radically underway. However, this implies that the processing of personal data is already on the verge of becoming universal.
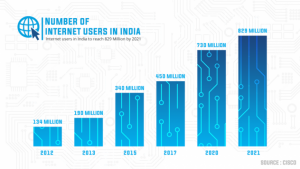
The population of mobile phone users in India has already crossed the 750 million mark. This number is expected to reach 490 million by 2022. Therefore, personal data and information become available in the public domain. Sources estimate that India has about 390 million millennials and about 440 million generation Z that follows millennials.
The Gen Z generation processes data faster. The most common use of this data is for mobile applications like Snapchat, Vine, and so on, apart from the usual popular social media apps. This leads to the creation of huge amounts of personal data for an individual — be it personal, behavioral, attitudinal, and financial. Which can essentially be used for both illegal and nefarious purposes, like what happened with Cambridge Analytica; Hence, data privacy will be of paramount importance in the coming years for governments across the world specifically to protect their citizens.
The IT Act 2000 — The First Ancestor Of Data Privacy
Under section 43A of the (Indian) Information Technology Act, 2000, a body corporate who is possessing, dealing, or handling any sensitive personal data or information, and is negligent in implementing and maintaining reasonable security practices resulting in wrongful loss or wrongful gain to any person, then such body corporate may be held liable to pay damages to the person so affected.
The Government of India has ratified the Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures and Sensitive Personal Data or Information) Rules, 2011. The Rules provide guidance against protection of “Sensitive personal data or information of a person”. This consists of such personal information which has information relating: –
- Passwords
- Financial information — Bank account or credit/debit card or other payment instrument information;
- Physical, physiological, and psychological health conditions;
- Sexual orientation
- Medical records and history;
- Biometric data.
Section 72 of the IT Act highlights the penalty for breach of confidentiality privacy. The Section provides that any person who, in pursuance of any of the powers conferred under the IT Act Rules or Regulations made thereunder, has secured access to any electronic record, book, register, correspondence, information, document, or other material without the consent of the person concerned, discloses such material to any other person, shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to two years, or with fine which may extend to Rs 1,00,000, (approx. US$ 3,000) or with both.
While the IT Act 2000 was not officially cleared for regulating data privacy in India. It can be considered as the stepping stone which laid the foundation for future legislature.
The Supreme Court Ruling of 2016- Amendment Of Data Privacy In Aadhaar Act
In 2016, India amended its biometric identification system, known as Aadhaar. This enabled both the government and private entities to collect an individual’s ID number for any purpose. Human rights advocates had decried this as a violation of privacy. There was a lot of concern and growing uncertainty surrounding this authorization. However, businesses in India continued to require ID numbers for certain services. It was also used for the ID numbers for consumer profiling and targeted advertisements.
The Supreme Court of India amended the 2016 Act which enabled private businesses to ask for customer ID numbers for any purpose. The Supreme Court was required to ascertain the validity of the provisions of the Aadhaar Act. The objective was to verify if the act was contrary to the right to privacy. This was later established as a fundamental right by the Supreme Court in 2017.
Key Findings in the Judgement
The judgment was unanimous with all nine judges concurring with the final order. However, six judges — Justice Chandrachud, Justice Nariman, Justice Chimaleshwar, Justice Kaul, Justice Sapre, and Justice Bobde, wrote separate opinions covering a wide range of issues.
The key points of the judgment are summarized below:
(a) Privacy — A Fundamental Right
The Supreme Court confirmed that the privacy rights of an individual are a fundamental right. It does not need to be separately articulated. It can be considered as a derivative of articles 14, 19, and 21 as mentioned in the Constitution of India. It is a right that subsists as a fundamental consequence of the right to life and liberty. It protects a person from the scrutiny of the State in their home, of their whereabouts, etc.
The same applies to more personal choices like reproductive choices, food habits, etc.
(b) Necessary But Not Absolute Right
The Supreme Court also highlighted that the fundamental right to privacy is not absolute. It will always be subject to considerable restrictions. The State can declare restrictions on the right to privacy to protect justifiable State interests. This can only be done by following the three-pronged method summarized below:
- Establishment of a law that rationalizes an encroachment on privacy
- A legitimate State aim or requirement which ensures that the nature of the composition of this law falls is reasonably valid. It should also operate to guard against arbitrary State action.
- The measures taken by the State are in tune with the objectives sought to be fulfilled by the law.
The Personal Data Protection Bill — India’s First Step To Legalize Data Privacy
Backdrop of The PDP Bill — How it came about
The Supreme Court observed during its judgment that privacy of personal data and facts is an essential aspect of the right to privacy.
Based on this, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) formed a 10-member committee led by retired Supreme Court judge B.N. Srikrishna. This committee was hence named the Srikrishna Committee. On 27 July 2018, the committee submitted an extensive draft which is now known as the Personal Data Protection Bill. India is now set to have a comprehensive personal data protection law. On 11.12.2019, MEITY introduced the Personal Data Protection Bill (PDP Bill) in Lok Sabha as Bill №373 of 2019.

The Birth Of PDP — India’s Data Privacy Bill
The PDP Bill seeks to provide for the protection of the personal data of individuals. It also intends to create a framework for processing such personal data. To do so, the bill proposes the establishment of a Data Protection Authority.
Key Takeaways of The PDP Bill
The following are the salient features of the Bill:
- The PDP Bill is meant to improve data handling and data privacy in a way that is similar to the European Union’s GDPR.
- The PDP Bill emphasizes the need to create a Data Protection Authority (DPA). This will be similar in fashion to the organizations present as part of the members of the European Union. The bill also defines the categories of sensitive personal data that require protection.
- The PDP Bill defines ‘data fiduciary’. It also proclaims the various obligations for them. These are based on how they shall obtain, deal/process, and retain personal data.
- If the PDP Bill becomes official, businesses would be required to inform users about their data collection practices. They would need the customers’ consent for the same as well. It would be their responsibility have to collect and store evidence of the fact that such notice was given and consent was received. The consumers would have the ability to withdraw their consent. This means that the businesses would have to design systems to allow clients to withdraw their consent on the same.
- The PDP Bill gives consumers the power to access, edit, and delete their data after the same is processed to fulfill its objective. As such, the businesses would have to create ways to allow consumers to do so.
- The PDP Bill enables clients to transfer their personal data. This can include any inferences made by businesses based on such data, to other businesses.
- The PDP Bill mandates all businesses to make changes on an organizational level to protect data better.
How PDP Inevitably Led To NPD
The PDP Bill stipulates that the Central Government can direct a data fiduciary or a data processor to provide anonymized personal data or non-personal data.
This can be done “to enable better targeting of delivery of services or formulation of evidence-based policies by Central Government”.
It was based on this that in September 2019, MeitY formed a committee of experts led by the co-founder of Infosys — Kris Gopalakrishnan. The purpose of the committee was to draft a framework to regulate non-personal data (NPD).
The NPD Framework
As stated above, the Indian government is considering a framework to regulate non-personal data (NPD). The Committee released its report on 12 July 2020 for public consultation/feedback.
A Brief Overview
The NPD framework could affect the entire value chain just like PDP. The impact could range from creators of tech services and products to enablers and consumers. The NPD framework will require companies to obtain user consent. This has to be done before anonymizing data and using it.
NPD includes data generated through online transactions. These can be orders through delivery platforms or any online service. The data is anonymized and all personal identifiers are removed. This data is then harnessed to enhance the quality of service, ML algorithms, and other technologies.
Non-Personal Data Authority — The New Player
There is an apparent need to regulate the collection, processing, storage, and sharing of NPD. For this, the Committee recommends the formation of a separate NPDA authority. The details on the constitution of the NPDA need to be figured out.
As of now, the Committee has highlighted that the NPDA should have some members with relevant industry experience. The Data Protection Authority (DPA) under the PDP Bill protects personal data. Similarly, the NPDA is meant to protect the value of NPD.
The NPDA should work simultaneously with the DPA. The same applies to other sectoral regulators like the Competition Commission of India. The Committee also advises that NPDA should play the roles of both enabler and enforcer.
As an enabler, the NPDA should ensure that NPD is available for various social, public, and economic purposes. This applies highly to legitimate NPD sharing requests. Other areas include:
- Regulate and supervise NPD sharing agreements between relevant stakeholders
- Supervise the market for NPD.
As an enforcer, the NPDA should overlook the provisions for the proposed NPD legislative affairs. This will include:
- Regulating Data Businesses
- Mandating the sharing of NPD in certain circumstances
- Setting standards and certifying frameworks, including for NPD sharing
- NPD safety
- Anonymization of PD.
Introduction Of “Data Business”
Under the NPD framework, the Committee advises that private and public sector entities who collect NPD be required to register as a Data Business. This will be dependent upon meeting certain criteria as per the guidelines of NPDA. For entities that do not meet these criteria, this registration will be voluntary. The Committee further recommended that this will be a one-time event. The process for registration will be lightweight and fully digital. The entities must provide details regarding their function. This includes the type of data they collect, process, and use. It also highlights the manner and purpose. To enhance the process, these disclosures will be made with respect to those relating to PD under the PDP Bill, if at all applicable.
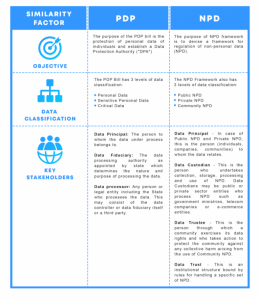
PDP and NPD — Similar Grounds
Similar to the classification of personal data under the PDP Bill, the committee classifies NPD into 3 categories namely general, sensitive, and critical categories. The framework also necessitates businesses to obtain user consent before anonymizing even NPD. For example, A cab aggregator wants to aggregate rider travel data from a section of the user base to derive insights. In this case, it would need consent from each rider in the cohort. Execution of this is bound to create practical challenges for companies. It will make analytics a lot more complicated for tech companies as well.
To know more about PDP stakeholders and details, click here
Key Stakeholders of NPD — An Elaborate Overview
The Report lists the following roles for potential players within the NPD framework:
(i) Data Principal — In the case of Public NPD and Private NPD, this is the person (individuals, companies, communities) to whom the data relates. In the case of Community NPD, the community that is the source of the NPD would be the Data Principal. This is similar to the categorization of a data principal under the PDP Bill, in relation to PD, with Data Principals being allowed to exercise significant control and economic rights over their NPD.
(ii) Data Custodian — This is the person who undertakes collection, storage, processing, and use of NPD. Data Custodians may be public or private sector entities who process NPD such as government ministries, telecom companies, or e-commerce entities. Data Custodians must comply with requirements under the NPD Legislation, such as adopting prescribed anonymization standards. NPD must be used by Data Custodians in a manner that is in the ‘best interest’ of the Data Principal. They have a ‘duty of care to the individual or community from which NPD has been collected. This principle is similar to that of a data fiduciary under the PDP Bill, which lays down specific obligations to be undertaken by the data fiduciary with respect to the data rights of the Data Principal.
(iii) Data Trustee — This is the person through which a community exercises its data rights and who takes action to protect the community against any collective harm arising from the use of Community NPD. In most instances, the Data Trustee will be the closest and most appropriate representative body for a community and maybe a government agency at any level (such as the Ministry of Health for data on diabetes in India). However, it could also be citizens’ groups (such as residents’ welfare associations for local data), or civil society organizations. However, there is no clarity provided as to how a Data Trustee would be identified, the eligibility criteria for such an entity, or whether the community data principals play a role in identifying the Data Trustee, and this is to be provided under the NPD Legislation.
(iv) Data Trust — This is an institutional structure bound by rules for handling a specific set of NPD. Such trusts may hold NPD which may be voluntarily shared by Data Custodians, or mandatorily shared NPD on the basis of orders from the government or Data Trustees (as described below in Section 8). However, the Committee has provided very little insight as to how Data Trusts will function, including how such trusts will be constituted, who determines its members, and its role in the NPD ecosystem.
Impact Of NPD — What This Means For Businesses
Tech companies or organizations that meet the currently undefined threshold of collected or processed data will be considered ‘data businesses’ under the proposed framework.
Such businesses will be subject to a host of compliance requirements, including registration, monitoring of operations, and disclosure obligations. They will have to submit metadata about the data they collect to open-access ‘meta-data directories — essentially sharing data on the data they collect.
Based on the above, anyone can query the business for their dataset. Quite obviously, there is a fear that even small companies and startups processing data could qualify as data businesses. Another point of concern is that they will be subject to excessive compliance and data-sharing framework. This will increase operational and data storage costs and hinder the ability of startups to develop their services.
The proposed framework could hamper business prospects by imposing mandatory sharing and a higher compliance burden. Given the absence of a global benchmark for NPD regulation, proposing specific legislation and a regulatory body for NPD without adequate consultation may be premature.
About Signzy
Signzy is a market-leading platform redefining the speed, accuracy, and experience of how financial institutions are onboarding customers and businesses – using the digital medium. The company’s award-winning no-code GO platform delivers seamless, end-to-end, and multi-channel onboarding journeys while offering customizable workflows. In addition, it gives these players access to an aggregated marketplace of 240+ bespoke APIs that can be easily added to any workflow with simple widgets.
Signzy is enabling ten million+ end customer and business onboarding every month at a success rate of 99% while reducing the speed to market from 6 months to 3-4 weeks. It works with over 240+ FIs globally, including the 4 largest banks in India, a Top 3 acquiring Bank in the US, and has a robust global partnership with Mastercard and Microsoft. The company’s product team is based out of Bengaluru and has a strong presence in Mumbai, New York, and Dubai.
Visit www.signzy.com for more information about us.
You can reach out to our team at reachout@signzy.com
Written By:
Signzy
Written by an insightful Signzian intent on learning and sharing knowledge.